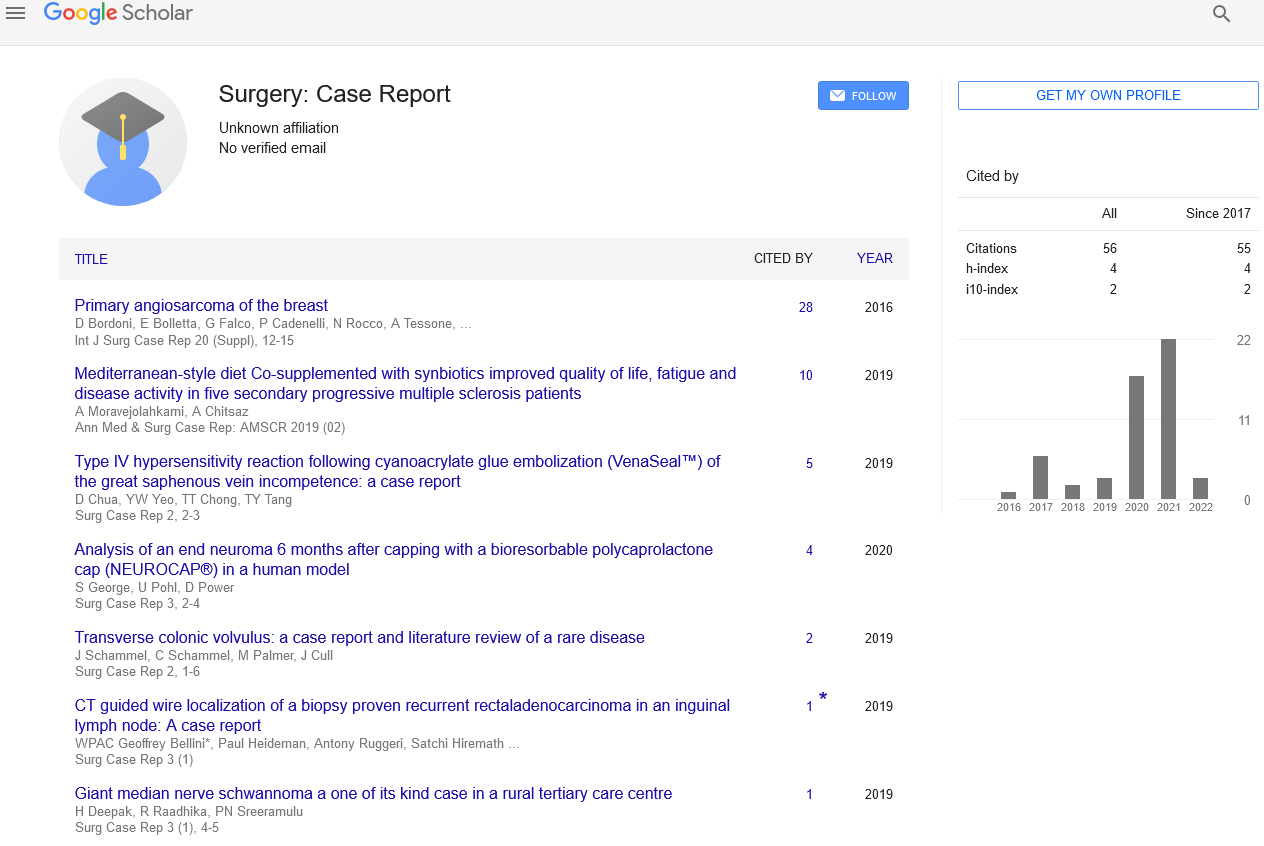
Sign up for email alert when new content gets added: Sign up
Prophylactic central neck dissection for clinically node-Negative papillary thyroid carcinoma
3rd WORLD CONGRESS ON OTOLARYNGOLOGY - HEAD AND NECK SURGERY
May 19, 2022 | Webinar
Sherif K. Abdelmoni, Mohammad A. Alessa, Haddad H. Alkaf, Amjad O. Aljohani, Reyan H. Merdad, Anas I. Alserif, Layan S. Alhemayed, Noor Z. Farsi, Thamer A. Alsufyani and Ameen Z. Alherabi
Ain Shams University, Egypt King Abdullah Medical City, Saudi Arabia Al-Farabi Private College for Dentistry and Nursing, Saudi Arabia King Saud Bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Saudi Arabia King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia Umm Al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia Taif University, Saudi Arabia Umm Al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Surg Case Rep
Abstract :
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that scrutinized the oncological benefits and postsurgical complications of total thyroidectomy (TT) plus prophylactic central neck dissection (pCND) versus TT alone among clinically node-negative (cN0) papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) patients. Methods: We screened five databases from inception to September 4, 2021 and evaluated the risk of bias of the eligible studies. We pooled dichotomous outcomes using the risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: Overall, we included 5 RCTs with low risk of bias comprising 795 patients (TT plus pCND = 410 and TT alone = 385). With regard to efficacy endpoint, the rate of structural loco-regional recurrence did not significantly differ between both groups (n =4RCTs,RR= 0.49, 95% CI [0.19, 1.27], P = .14). With regard to safety endpoints, the rates of hypoparathyroidism (n = 5 RCTs, RR = 1.48, 95% CI [0.73, 2.97], P = .27), recurrent laryngeal nerve injury (n = 5RCTs,RR= 1.34, 95% CI [0.59, 3.03], P =.48) and bleeding (n = 3RCTs,RR= 1.75, 95% CI [0.42, 7.26], P = .44) did not significantly differ between both groups. Conclusion: For cN0 PTC patients, there was no significant difference between TT plus pCND and TT alone with regard to the rate of structural loco-regional recurrence or frequency of postsurgical complications. Adaptation of pCND in cN0 PTC patients should be contemplated by taking into consideration the clinical oncological benefits and rate of postsurgical adverse events. Key Words: Prophylactic central neck dissection, total thyroidectomy, papillary thyroid cancer, randomized controlled trials, meta-analysis. Level of Evidence: 1 Recent Publications 1. Validity and Reliability of an Arabic Version of MD Anderson Dysphagia Inventory (MDADI) 2. The impact of thyroid tumor features on lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma patients in head and neck department at KAMC: A retrospective cross-sectional study 3. Left Thyroid Agenesis Case Study Case Report
Biography :
Sherif K Abdelmonim is currently working in the Ain Shams University, Egypt.