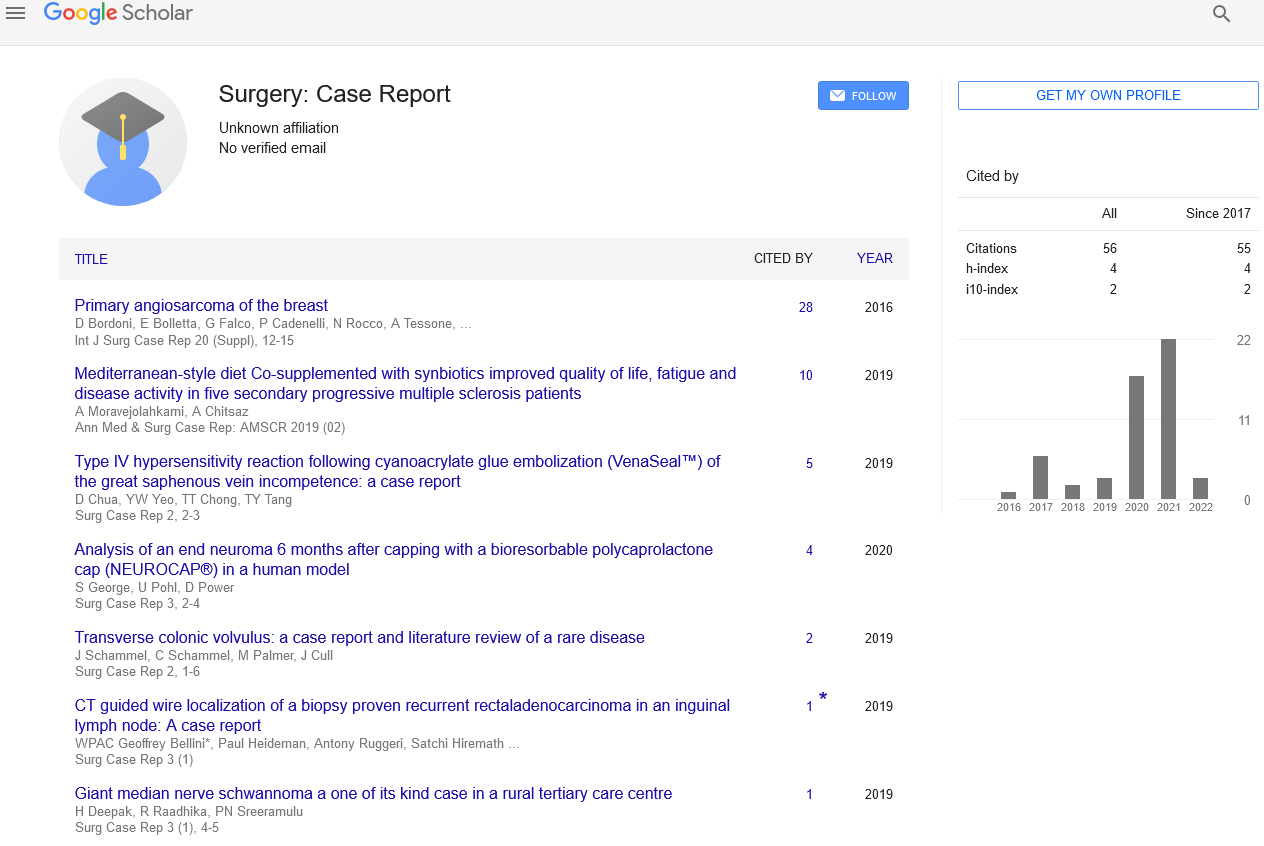
Sign up for email alert when new content gets added: Sign up
Protective effect of a lateral hinge screw for medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy in a sawbones model: a matched comparison study
16th International Conference on Orthopaedics, Arthroplastyt and Arthroscopy
June 29, 2023 | Webinar
Wiemi A Douoguih
Regional Medical Director of MedStar Sports Medicine, USA
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Surg Case Rep
Abstract :
Lateral hinge fracture (LHF) occurs in up to 30% of medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy (MOWHTO) cases. LHF can lead to delayed union, correction loss, and pseudo-arthrosis. Recently, a protective hinge wire intersecting the osteotomy plane was shown to increase resistance to hinge fracture by 880% and nearly doubled the angle of correction before fracture. While intraoperative LHF can be decreased with the use of a laterally based wire, no studies have elucidated the protective effect that a hinge screw would confer in simulated postoperative loading. We hypothesize the lateral hinge would increase the resistance to varus stress. Methods: In vitro biomechanical testing was conducted utilizing the MTS where varus stress was applied to specimens along the tibial shaft after being mounted proximally at the tibial plateau. Sawbones were prepared with a proprietary patient specific cutting guide to create a standardized 6-degree biplanar MOWHTO. A protective hinge wire was placed through the guide to prevent LHF during opening of the osteotomy. In 6 of the 12 specimens, a protective antegrade 4.0 mm cannulated screw was placed from the proximal lateral tibial plateau within 1 cm of the lateral tibial cortex. In the remaining 6 specimens the hinge wire was removed after the osteotomy was secured, without hinge screw constituting the control group. Varus load was applied continuously until lateral hinge fracture occurred in all 12 specimens. Results: The maximum load to hinge breakage was statistically higher in the hinge screw group compared to the control group (437 N vs 336 N, p = 0.046). Load to failure was 76% higher in MOWHTO using a hinge screw versus the control. Conclusions: This study demonstrated that during MOWHTO, screw fixation at the lateral hinge location increased construct resistance to varus stress. Recent Publications: 1. Douoguih WA. Zade R, Bodendorfer B, Siddiqi Y. Outcomes of Selective ACL Repair of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament with Suture Augmentation. Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation Aug 2020. 2. Bachmaier S, DiFelice, GS, Sonnery-Cottet B, Douoguih WA, Smith PA, Pace LJ, Ritter D, Wijdicks CA. Treatment of Acute Proximal Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears- Part 1: Gap Formation and Stabilization Potential of Repair Techniques. Orthopedic Journal of Sports Med. January 2020; 8 (1). 3. Bachmaier S, DiFelice, GS, Sonnery-Cottet B, Douoguih WA, Smith PA, Pace LJ, Ritter D, Wijdicks CA. Treatment of Acute Proximal Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears- Part 2: The Role of Internal Bracing on Gap Formation and Stabilization of Repair Techniques Orthopedic Journal of Sports Med January 2020; 8 (1).