A rare variation in the branching pattern of posterior cord
Ahmet Dursun, Cemil Bilkay, Soner Albay*
Suleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Anatomy, Isparta, Turkey.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Soner Albay, MD
Assoc. Prof. of Anatomy, Suleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Anatomy, 32260 Isparta / Turkey
Tel: +90 246 2113680
E-mail: sujan.ganapathy@gmail.com
Date of Received: December 9th, 2014
Date of Accepted: August 16th, 2016
Published Online: August 17th, 2016
© Int J Anat Var (IJAV). 2016; 9: 29–31.
[ft_below_content] =>Keywords
posterior cord, subscapular nerves, thoracodorsal nerve, axillary nerve, variation
Introduction
The brachial plexus has a complex structure and is in close relationship with the important anatomical structures. Thus, variations of the brachial plexus have significant clinical and surgical importance [1]. Most of the data describing variations from the standard anatomic structure of the brachial plexus are derived from anatomic dissections, with up to 53% of the plexuses studied demonstrating significant anatomic variations [1].
The brachial plexus is fully developed by the 13th week of gestation [2]. Early in development, the successive anterior primary rami supplying the limb buds are joined by connecting loops to form the cervico-brachial plexus. These nerves grow into the muscles and follow them as they migrate caudally into the limb. There is an intrinsic migration of individual muscles too. The muscles split into a ventral/flexor group and a dorsal/extensor group. Likewise, the posterior divisions of these trunks supply the extensor muscles, while anterior divisions supply the flexors. Changes in the pattern of migration can result in modification of the primitive segmental arrangement of nerves or their loops forming the brachial plexus [3]. Brachial plexus usually was formed by the union of the ventral primary rami of the spinal nerves, C5–C8 and T1, the so-called “roots” of the brachial plexus. The roots form trunks. Anterior and posterior divisions of the trunks unite in a systematic manner to form three cords, i.e., lateral, medial and posterior cords; named according to their position relative to second part of axillary artery [4]. Ballesteros et al., Fazan et al. and Muthako et al. have displayed variations of the posterior cord in their studies. Standard medical textbooks describe that the upper subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve and the lower subscapular nerve are derived from the posterior cord, and two terminal branches of the posterior cord are axillary and radial nerves. Variations of the brachial plexus are not uncommon. Variations have been reported about branches of the posterior cord and the distribution of the branches.
Case Report
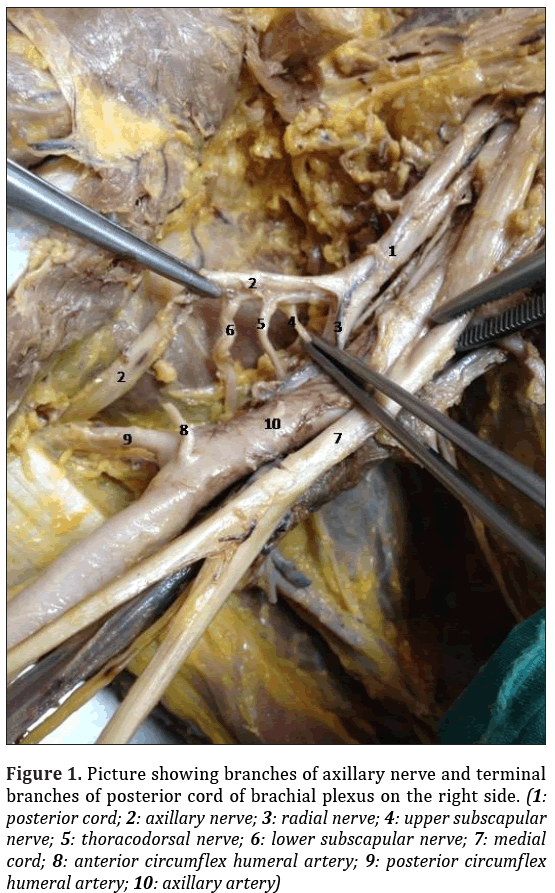
During routine dissection for undergraduate teaching, variation of the brachial plexus was found in the right upper extremity of a 72-year-old formalin-fixed female cadaver who had no pathological or traumatic lesions, or surgical scar in the neck, thoracic or axillary region. In left upper extremity, brachial plexus, axillary artery and neighborhoods of brachial plexus showed no variations. In the right upper extremity, axillary artery and neighborhoods of brachial plexus showed no variations. Formations of medial, superior and inferior trunks and branches of all trunks were as usual in the right side. Lateral, medial cords and terminal branches of lateral, medial cords were observed as identified in classical textbooks. Posterior cord did not branch and formed two terminal branches which were axillary nerve and radial nerve. Radial nerve was normal in anatomy and lying in normal position but the upper subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve and the lower subscapular nerve emanated from axillary nerve (Figure 1). This branches with variant origins were in usual anatomical position and course.
Figure 1: Picture showing branches of axillary nerve and terminal branches of posterior cord of brachial plexus on the right side. (1: posterior cord; 2: axillary nerve; 3: radial nerve; 4: upper subscapular nerve; 5: thoracodorsal nerve; 6: lower subscapular nerve; 7: medial cord; 8: anterior circumflex humeral artery; 9: posterior circumflex humeral artery; 10: axillary artery)
Discussion
The knowledge on the variations of brachial plexus is very important for anesthetic blockage, surgical interventions and radiological examination of the region. The interpretation of a nervous compression having unexplained clinical symptoms (sensory loss, pain, wakefulness and paresis) and these structures being compromised represent the clinical importance of these variations [5].
Trauma of the posterior wall of the axillary region could impair latissimus dorsi muscle function (humeral movement extension, adduction and medial rotation), depending on level of the lesion and the involvement of its several origins. For instance, an axillary nerve lesion engaging the thoracodorsal nerve origin may cause a more extensive functional lesion including latissimus dorsi, deltoid and teres minor muscles [5].
Standard medical textbooks describe that upper subscapular, thoracodorsal and lower subscapular nerves deriving from the posterior cord. In our case, upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve and lower subscapular nerve were derived from axillary nerve on the right side.
Similar variations in previously published studies and case reports are summarized in Table 1. Ballesteros et al. studied with 57 cadaver specimens and found 54.4% of the lower subscapular nerves originating from the axillary nerve, 5.4% of the upper subscapular nerves originating from the axillary nerve, and 8.9% of the thoracodorsal nerves originating from the axillary nerve [5]. Fazan et al. studied with 27 human cadavers and found 54% of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, 5.5% of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and 13% of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [6]. Mutoka et al. studied with 68 human cadavers and found 57.3% of the lower subscapular nerves having origin from the axillary nerve, 13.3% of the upper subscapular nerves from the axillary nerve, and 10.7% of the thoracodorsal nerves from the axillary nerve [7]. Tubbs et al. studied with 31 human cadavers and found 21% of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, 3% of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and none of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [8]. Rastogi et al. studied with 37 human cadavers and found none of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, none of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and 22.9% of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [9]. Chaudhary et al. studied with 30 human cadavers and found 3.3% of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, none of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and none of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [10]. However, none of these studies included all of these nerves (the lower subscapular nerve, the upper subscapular nerve and the thoracodorsal nerve) arising from the axillary nerve, as in the present case. to the best of our knowledge, such a variation has not been reported in the literature up to date.
| Reference | Population | Number of cases | Lower subscapular nerve originated from the axillary nerve (%) | Upper subscapular nerve originated from the axillary nerve (%) | Thoracodorsal nerve originated from the axillary nerve (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ballesteros et al. [5] | Colombia | 57 | 54.4 | 5.4 | 8.9 |
| Fazan et al. [6] | Brazil | 54 | 54 | 5.5 | 13 |
| Muthoka et al. [7] | Kenya | 136 | 57.3 | 13.3 | 10.7 |
| Tubbs et al. [8] | USA | 62 | 21 | 3 | 0 |
| Rastogi et al. [9] | India | 74 | 0 | 0 | 22.9 |
| Chaudhary et al. [10] | India | 60 | 3.33 | 0 | 0 |
Table 1: Variations of origin of thoracodorsal, upper and lower subscapular nerves in different studies.
Thus, the knowledge of the lower subscapular nerve, the upper subscapular nerve and the thoracodorsal nerve emerging from the axillary nerve is very important for successful regional anesthesia, surgical interventions and radiological examination in this region.
References
- Johnson EO, Vekris M, Demesticha T, Soucacos PN. Neuroanatomy of the brachial plexus: normal and variant anatomy of its formation. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32: 291–297.
- Pellerin M, Kimball Z, Tubbs RS, Nguyen S, Matuzs P, Cohen-Gadol AA, Loukas M. The prefixed and postfixed brachial plexus: a review with surgical implications. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32: 251–260.
- Khodke P, Ambiye M, Khambatta S. Absent posterior cord of brachial plexus with third head of biceps brachii. Int J Anat Var. 2013; 6: 77–80.
- Aggarwal A, Puri N, Aggarwal AK, Harjeet K, Sahni D. Anatomical variation in formation of brachial plexus and its branching. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32: 891–8944.
- Ballesteros LE, Ramirez LM. Variations of the origin of collateral branches emerging from the posterior aspect of the brachial plexus. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2007; 6: 1–6.
- Fazan VPS, Amadeu A de S, Caleffi AL, Rodrigues Filho OA. Brachial plexus variations in its formation and main branches. Acta Cir Bras. 2003; 18: 14–18.
- Muthoka JM, Sinkeet SR, Shahbal SH, Matakwa LC, Ogeng’o J. Variations in branching of the posterior cord of brachial plexus in a Kenyan population. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2011; 6: 1-5.
- Tubbs RS, Loukas M, Shahid K, Judge T, Pinyard J, Shoja MM, Slappey JB, Mcovey WC, Oakes WJ. Anatomy and quantitation of the subscapular nerves. Clin Anat. 2007; 20: 656–659.
- Rastogi R, Budhiraja V, Bansal K. Posterior cord of brachial plexus and its branches: Anatomical variations and clinical implication. ISRN Anatomy. 2013; Article ID 501813.
- Chaudhary P, Singla R, Kalsey G, Arora K. Branching pattern of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus: A cadaveric study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2011; 5: 787–790.
Ahmet Dursun, Cemil Bilkay, Soner Albay*
Suleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Anatomy, Isparta, Turkey.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Soner Albay, MD
Assoc. Prof. of Anatomy, Suleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Anatomy, 32260 Isparta / Turkey
Tel: +90 246 2113680
E-mail: sujan.ganapathy@gmail.com
Date of Received: December 9th, 2014
Date of Accepted: August 16th, 2016
Published Online: August 17th, 2016
© Int J Anat Var (IJAV). 2016; 9: 29–31.
Abstract
Variations have been reported about branches of the brachial plexus and the distribution of the branches, but variations of posterior cord are partly rare. Variation of the brachial plexus was found in the right upper extremity of a 72-year-old formalin-fixed female cadaver who had no pathological or traumatic lesions, or surgical scar in the neck, thoracic or axillary region. In the right brachial plexus, it was observed that posterior cord had only two branches, namely axillary and radial nerves. Upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve and lower subscapular nerve emanated from axillary nerve. There was no other variation of brachial plexus in either side. The knowledge of the lower subscapular nerve, the upper subscapular nerve and the thoracodorsal nerve emerging from the axillary nerve is very important for successful regional anesthesia, surgical interventions and radiological examination in this region.
-Keywords
posterior cord, subscapular nerves, thoracodorsal nerve, axillary nerve, variation
Introduction
The brachial plexus has a complex structure and is in close relationship with the important anatomical structures. Thus, variations of the brachial plexus have significant clinical and surgical importance [1]. Most of the data describing variations from the standard anatomic structure of the brachial plexus are derived from anatomic dissections, with up to 53% of the plexuses studied demonstrating significant anatomic variations [1].
The brachial plexus is fully developed by the 13th week of gestation [2]. Early in development, the successive anterior primary rami supplying the limb buds are joined by connecting loops to form the cervico-brachial plexus. These nerves grow into the muscles and follow them as they migrate caudally into the limb. There is an intrinsic migration of individual muscles too. The muscles split into a ventral/flexor group and a dorsal/extensor group. Likewise, the posterior divisions of these trunks supply the extensor muscles, while anterior divisions supply the flexors. Changes in the pattern of migration can result in modification of the primitive segmental arrangement of nerves or their loops forming the brachial plexus [3]. Brachial plexus usually was formed by the union of the ventral primary rami of the spinal nerves, C5–C8 and T1, the so-called “roots” of the brachial plexus. The roots form trunks. Anterior and posterior divisions of the trunks unite in a systematic manner to form three cords, i.e., lateral, medial and posterior cords; named according to their position relative to second part of axillary artery [4]. Ballesteros et al., Fazan et al. and Muthako et al. have displayed variations of the posterior cord in their studies. Standard medical textbooks describe that the upper subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve and the lower subscapular nerve are derived from the posterior cord, and two terminal branches of the posterior cord are axillary and radial nerves. Variations of the brachial plexus are not uncommon. Variations have been reported about branches of the posterior cord and the distribution of the branches.
Case Report
During routine dissection for undergraduate teaching, variation of the brachial plexus was found in the right upper extremity of a 72-year-old formalin-fixed female cadaver who had no pathological or traumatic lesions, or surgical scar in the neck, thoracic or axillary region. In left upper extremity, brachial plexus, axillary artery and neighborhoods of brachial plexus showed no variations. In the right upper extremity, axillary artery and neighborhoods of brachial plexus showed no variations. Formations of medial, superior and inferior trunks and branches of all trunks were as usual in the right side. Lateral, medial cords and terminal branches of lateral, medial cords were observed as identified in classical textbooks. Posterior cord did not branch and formed two terminal branches which were axillary nerve and radial nerve. Radial nerve was normal in anatomy and lying in normal position but the upper subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve and the lower subscapular nerve emanated from axillary nerve (Figure 1). This branches with variant origins were in usual anatomical position and course.
Figure 1: Picture showing branches of axillary nerve and terminal branches of posterior cord of brachial plexus on the right side. (1: posterior cord; 2: axillary nerve; 3: radial nerve; 4: upper subscapular nerve; 5: thoracodorsal nerve; 6: lower subscapular nerve; 7: medial cord; 8: anterior circumflex humeral artery; 9: posterior circumflex humeral artery; 10: axillary artery)
Discussion
The knowledge on the variations of brachial plexus is very important for anesthetic blockage, surgical interventions and radiological examination of the region. The interpretation of a nervous compression having unexplained clinical symptoms (sensory loss, pain, wakefulness and paresis) and these structures being compromised represent the clinical importance of these variations [5].
Trauma of the posterior wall of the axillary region could impair latissimus dorsi muscle function (humeral movement extension, adduction and medial rotation), depending on level of the lesion and the involvement of its several origins. For instance, an axillary nerve lesion engaging the thoracodorsal nerve origin may cause a more extensive functional lesion including latissimus dorsi, deltoid and teres minor muscles [5].
Standard medical textbooks describe that upper subscapular, thoracodorsal and lower subscapular nerves deriving from the posterior cord. In our case, upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve and lower subscapular nerve were derived from axillary nerve on the right side.
Similar variations in previously published studies and case reports are summarized in Table 1. Ballesteros et al. studied with 57 cadaver specimens and found 54.4% of the lower subscapular nerves originating from the axillary nerve, 5.4% of the upper subscapular nerves originating from the axillary nerve, and 8.9% of the thoracodorsal nerves originating from the axillary nerve [5]. Fazan et al. studied with 27 human cadavers and found 54% of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, 5.5% of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and 13% of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [6]. Mutoka et al. studied with 68 human cadavers and found 57.3% of the lower subscapular nerves having origin from the axillary nerve, 13.3% of the upper subscapular nerves from the axillary nerve, and 10.7% of the thoracodorsal nerves from the axillary nerve [7]. Tubbs et al. studied with 31 human cadavers and found 21% of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, 3% of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and none of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [8]. Rastogi et al. studied with 37 human cadavers and found none of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, none of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and 22.9% of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [9]. Chaudhary et al. studied with 30 human cadavers and found 3.3% of the lower subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve, none of the upper subscapular nerves originated from the axillary nerve and none of the thoracodorsal nerves originated from the axillary nerve [10]. However, none of these studies included all of these nerves (the lower subscapular nerve, the upper subscapular nerve and the thoracodorsal nerve) arising from the axillary nerve, as in the present case. to the best of our knowledge, such a variation has not been reported in the literature up to date.
| Reference | Population | Number of cases | Lower subscapular nerve originated from the axillary nerve (%) | Upper subscapular nerve originated from the axillary nerve (%) | Thoracodorsal nerve originated from the axillary nerve (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ballesteros et al. [5] | Colombia | 57 | 54.4 | 5.4 | 8.9 |
| Fazan et al. [6] | Brazil | 54 | 54 | 5.5 | 13 |
| Muthoka et al. [7] | Kenya | 136 | 57.3 | 13.3 | 10.7 |
| Tubbs et al. [8] | USA | 62 | 21 | 3 | 0 |
| Rastogi et al. [9] | India | 74 | 0 | 0 | 22.9 |
| Chaudhary et al. [10] | India | 60 | 3.33 | 0 | 0 |
Table 1: Variations of origin of thoracodorsal, upper and lower subscapular nerves in different studies.
Thus, the knowledge of the lower subscapular nerve, the upper subscapular nerve and the thoracodorsal nerve emerging from the axillary nerve is very important for successful regional anesthesia, surgical interventions and radiological examination in this region.
References
- Johnson EO, Vekris M, Demesticha T, Soucacos PN. Neuroanatomy of the brachial plexus: normal and variant anatomy of its formation. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32: 291–297.
- Pellerin M, Kimball Z, Tubbs RS, Nguyen S, Matuzs P, Cohen-Gadol AA, Loukas M. The prefixed and postfixed brachial plexus: a review with surgical implications. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32: 251–260.
- Khodke P, Ambiye M, Khambatta S. Absent posterior cord of brachial plexus with third head of biceps brachii. Int J Anat Var. 2013; 6: 77–80.
- Aggarwal A, Puri N, Aggarwal AK, Harjeet K, Sahni D. Anatomical variation in formation of brachial plexus and its branching. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32: 891–8944.
- Ballesteros LE, Ramirez LM. Variations of the origin of collateral branches emerging from the posterior aspect of the brachial plexus. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2007; 6: 1–6.
- Fazan VPS, Amadeu A de S, Caleffi AL, Rodrigues Filho OA. Brachial plexus variations in its formation and main branches. Acta Cir Bras. 2003; 18: 14–18.
- Muthoka JM, Sinkeet SR, Shahbal SH, Matakwa LC, Ogeng’o J. Variations in branching of the posterior cord of brachial plexus in a Kenyan population. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2011; 6: 1-5.
- Tubbs RS, Loukas M, Shahid K, Judge T, Pinyard J, Shoja MM, Slappey JB, Mcovey WC, Oakes WJ. Anatomy and quantitation of the subscapular nerves. Clin Anat. 2007; 20: 656–659.
- Rastogi R, Budhiraja V, Bansal K. Posterior cord of brachial plexus and its branches: Anatomical variations and clinical implication. ISRN Anatomy. 2013; Article ID 501813.
- Chaudhary P, Singla R, Kalsey G, Arora K. Branching pattern of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus: A cadaveric study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2011; 5: 787–790.