Equivalence of energy and time
Received: 27-Mar-2023, Manuscript No. puljpam-23-6309; Editor assigned: 28-Mar-2023, Pre QC No. puljpam-23-6309 (PQ); Reviewed: 29-Mar-2023 QC No. puljpam-23-6309 (Q); Revised: 30-Mar-2023, Manuscript No. puljpam-23-6309 (R); Published: 31-Mar-2023, DOI: 10.37532/2752-8081.23.7(2).139
Citation: Jöge FM. Equivalence of energy and time. J Pure Appl Math. 2023; 7(2):139
This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits reuse, distribution and reproduction of the article, provided that the original work is properly cited and the reuse is restricted to noncommercial purposes. For commercial reuse, contact reprints@pulsus.com
Introduction
A formula is developed that shows the equivalence of energy and time.
Derivation of a formula that describes the equivalence of energy and time.
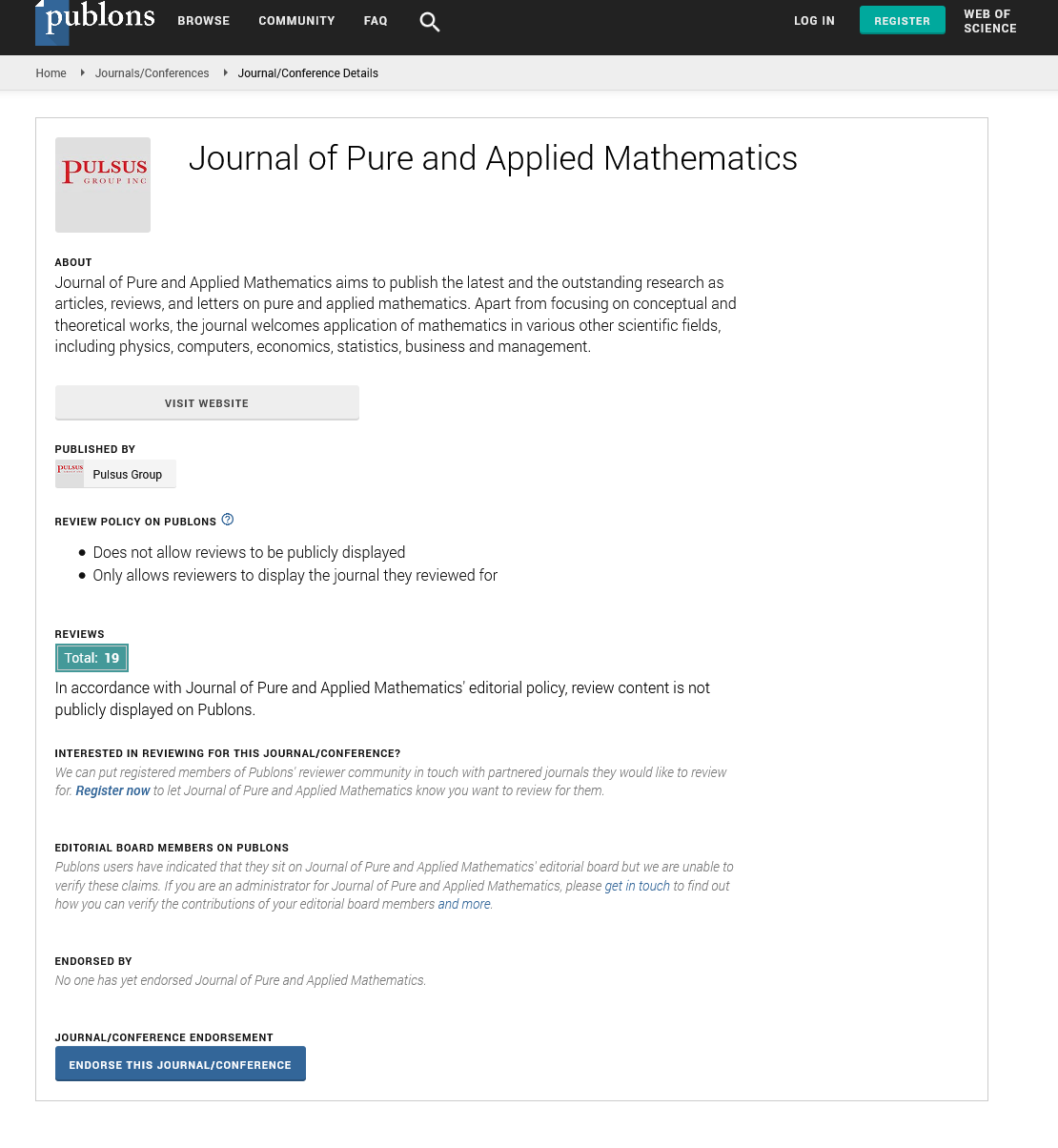
A formula for calculation dark energy was developed under the title „Calculation of Dark Energy and Dark Matter“. It is:
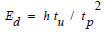
This formula is now expanded below to
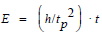
Starting from E = h/t is obtained by substituting tp for t
Ep = h/tp for the energy in the Planck time.
For the energy per one second we get:
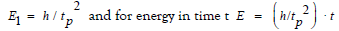
This is the general formula for the equivalence of energy and time. If you use the age of the universe for the time t, you get the amount of dark energy [1-2].
Definition of symbols used in formulas
E = energy
Ed = dark energy
t = time
tu = age of the universe
tp = Planck time
h = Planck quantum action
References
- Jöge FM. Calculation of Dark Energy and Dark Matter. Int J Phy Ast. 2019:7(1); 01-07
[Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Kinseher Richard. Das Wesen von Zeit ist Energie, Verlag Books on Demand GmbH. 2016
[Google Scholar] [Crossref]