Kirk’s arcade: a case report
David Ebeneizer1, Jiji PJ2*, Rajanigandha Vadgaonkar2, Latha V Prabhu2, Mamatha Tonse2, Aarathi Venunadan3
1Department of Anatomy, K. S. Hegde Medical Academy, Deralakatte, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
2Department of Anatomy, Centre for Basic Sciences, Bejai, Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
3Department of Anatomy, Yenepoya Medical College, Deralakatte, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Jiji PJ, MSc
Sr. Grade Lecturer, Department of Anatomy, Centre for Basic Sciences, Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore, Manipal University, Karnataka, 575004, India.
Tel: +91 824 2211746
E-mail: pj.jiji@gmail.com
Date of Received: March 20th, 2009
Date of Accepted: July 10th, 2009
Published Online: August 5th, 2009
© IJAV. 2009; 2: 78–79.
[ft_below_content] =>Keywords
dorsal pancreatic artery, Kirk’s arcade, coeliac trunk, inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
Introduction
The dorsal pancreatic artery (DPA) is nearly always present. Regarding variations in the origin of DPA, Bergman et al. reported that the DPA arose from the splenic artery in 37%, coeliac trunk in 33%, superior mesenteric artery in 21% and common hepatic artery in 8% of cases [1]. The right branch of the DPA joins together with anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery or gastroduodenal artery to form the Kirk’s arcade [2]. Woodburne and Olsen found the right branch of DPA emerging onto the anterior surface of the head of the pancreas and forming Kirk’s arcade in 93.3% of the cases in which it was present [3].
Case Report
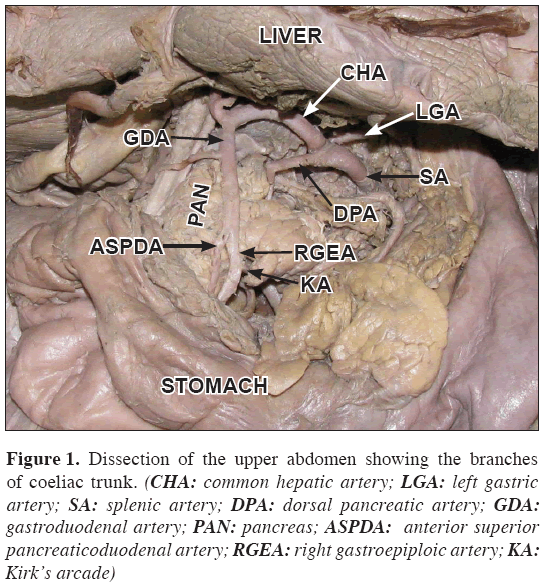
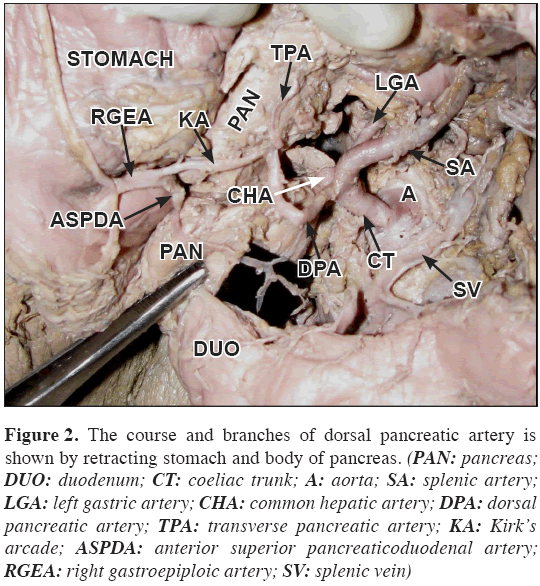
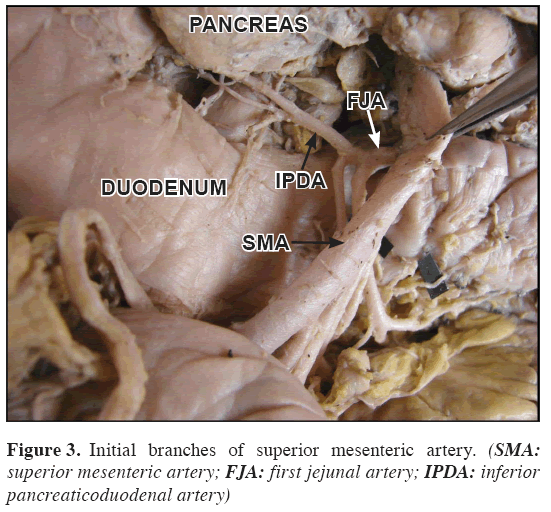
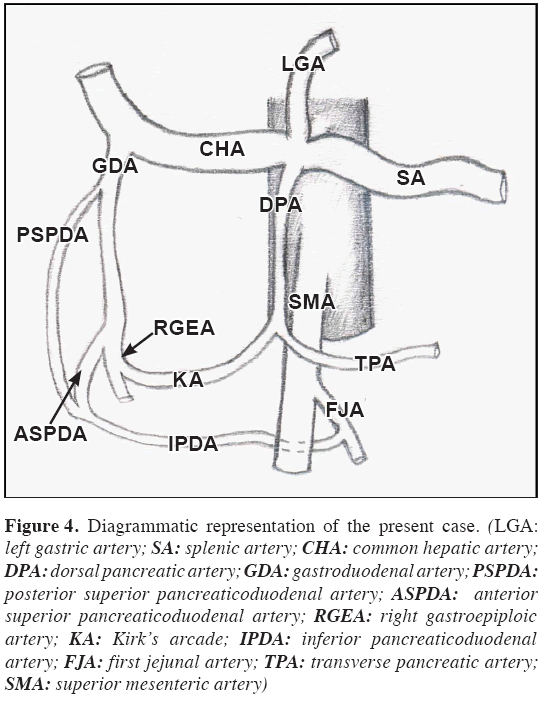
During routine dissection of a 50-year-old female cadaver, the DPA was found arising from the coeliac trunk directly (Figure 1). It passed downward dorsal to the neck of the pancreas and splenic vein; it ended by dividing into right and left branches close to the inferior border of pancreas (Figure 2). The right branch which usually anastomoses with the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery, in this case anastomosed with right gastroepiploic artery close to its origin forming the Kirk’s arcade. The left branch coursed along the inferior border of the pancreas on its dorsal surface as the transverse pancreatic artery. It was also found that the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (IPDA) and the first jejunal branch arose from a common trunk from the superior mesenteric artery (Figure 3). A diagrammatic representation of the present case is included (Figure 4).
Figure 1: Dissection of the upper abdomen showing the branches of coeliac trunk. (CHA: common hepatic artery; LGA: left gastric artery; SA: splenic artery; DPA: dorsal pancreatic artery; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; PAN: pancreas; ASPDA: anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; RGEA: right gastroepiploic artery; KA: Kirk’s arcade)
Figure 2: The course and branches of dorsal pancreatic artery is shown by retracting stomach and body of pancreas. (PAN: pancreas; DUO: duodenum; CT: coeliac trunk; A: aorta; SA: splenic artery; LGA: left gastric artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; DPA: dorsal pancreatic artery; TPA: transverse pancreatic artery; KA: Kirk’s arcade; ASPDA: anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; RGEA: right gastroepiploic artery; SV: splenic vein)
Figure 4: Diagrammatic representation of the present case. (LGA: left gastric artery; SA: splenic artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; DPA: dorsal pancreatic artery; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; PSPDA: posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; ASPDA: anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; RGEA: right gastroepiploic artery; KA: Kirk’s arcade; IPDA: inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery; FJA: first jejunal artery; TPA: transverse pancreatic artery; SMA: superior mesenteric artery)
Discussion
Knowledge of variations of upper abdominal arteries is important while dealing with gastric and duodenal ulcers, biliary tract surgeries and mobilization of the head of pancreas; since bleeding is one of the complications of these surgeries. According to Michels, when ligation of the common hepatic artery for hepatic arterial aneurysm or portal hypertension is made proximal to the gastroduodenal artery, collateral circulation routed through the Kirk’s arcade may reach the liver for maintenance of life sustaining blood to the organ. Since survival following ligation of hepatic artery is dependent upon the level of the ligation; presence of variant vessels, the extent of development of a true collateral circulation from arteries other than the hepatic, and the efficacy of these arcades needs to be established [4]. During pancreaticoduodenectomies or lymph node resection procedures, ligation of IPDA also requires special attention, because of the high incidence of common trunk formation of the first jejunal and IPDA [5]. Taken into consideration the facts that DPA lies at the vascular junction between coeliac trunk and superior mesenteric artery with variable origin and extent, its major role in pancreatic supply, and Kirk’s arcade is almost consistent feature of it, its efficacy as a collateral pathway needs to be evaluated along with that of the cephalic pancreaticoduodenal arcades in surgeries of pancreas or liver.
References
- Bergman RA, Thompson SA, Afifi AK, Saadeh FA. Compendium of Human Anatomic Variation. Baltimore – Munich, Urban & Schwarzenberg. 1988; 79.
- Kirk E. Untersuchungen über die gröbere end feineretopographische Verteilung der Arterien, Venen uns Ausführungsgänge in der menschlichen Bauchspeicheldrüse. Z Ges Anat. 1931; 94: 822–875. (German)
- Woodburne RT, Olsen LL. The arteries of the pancreas. Anat Rec. 1951; 111: 255–270.
- Michels NA. Collateral arterial pathways to the liver after ligation of the hepatic artery and removal of the celiac axis. Cancer. 1953; 6: 708–724.
- Murakami G, Hirata K, Takamuro T, Mukaiya M, Hata F, Kitagawa S. Vascular anatomy of the pancreatico-duodenal region: A review. J Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Surg. 1999; 6: 55–68.
David Ebeneizer1, Jiji PJ2*, Rajanigandha Vadgaonkar2, Latha V Prabhu2, Mamatha Tonse2, Aarathi Venunadan3
1Department of Anatomy, K. S. Hegde Medical Academy, Deralakatte, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
2Department of Anatomy, Centre for Basic Sciences, Bejai, Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
3Department of Anatomy, Yenepoya Medical College, Deralakatte, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Jiji PJ, MSc
Sr. Grade Lecturer, Department of Anatomy, Centre for Basic Sciences, Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore, Manipal University, Karnataka, 575004, India.
Tel: +91 824 2211746
E-mail: pj.jiji@gmail.com
Date of Received: March 20th, 2009
Date of Accepted: July 10th, 2009
Published Online: August 5th, 2009
© IJAV. 2009; 2: 78–79.
Abstract
A variation in the branching of the coeliac trunk was found in which the coeliac trunk gave four arteries, the common hepatic, splenic, left gastric and an additional dorsal pancreatic artery. One of the branches of the dorsal pancreatic artery joined with the right gastroepiploic artery close to its origin to form Kirk’s arcade. The clinical implication is that the location and course of dorsal pancreatic artery should be established given its central role in blood supply of the pancreas. The presence of Kirk’s arcade also needs to be evaluated as it can establish a collateral pathway for blood to reach the liver in common hepatic arterial occlusions.
-Keywords
dorsal pancreatic artery, Kirk’s arcade, coeliac trunk, inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
Introduction
The dorsal pancreatic artery (DPA) is nearly always present. Regarding variations in the origin of DPA, Bergman et al. reported that the DPA arose from the splenic artery in 37%, coeliac trunk in 33%, superior mesenteric artery in 21% and common hepatic artery in 8% of cases [1]. The right branch of the DPA joins together with anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery or gastroduodenal artery to form the Kirk’s arcade [2]. Woodburne and Olsen found the right branch of DPA emerging onto the anterior surface of the head of the pancreas and forming Kirk’s arcade in 93.3% of the cases in which it was present [3].
Case Report
During routine dissection of a 50-year-old female cadaver, the DPA was found arising from the coeliac trunk directly (Figure 1). It passed downward dorsal to the neck of the pancreas and splenic vein; it ended by dividing into right and left branches close to the inferior border of pancreas (Figure 2). The right branch which usually anastomoses with the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery, in this case anastomosed with right gastroepiploic artery close to its origin forming the Kirk’s arcade. The left branch coursed along the inferior border of the pancreas on its dorsal surface as the transverse pancreatic artery. It was also found that the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (IPDA) and the first jejunal branch arose from a common trunk from the superior mesenteric artery (Figure 3). A diagrammatic representation of the present case is included (Figure 4).
Figure 1: Dissection of the upper abdomen showing the branches of coeliac trunk. (CHA: common hepatic artery; LGA: left gastric artery; SA: splenic artery; DPA: dorsal pancreatic artery; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; PAN: pancreas; ASPDA: anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; RGEA: right gastroepiploic artery; KA: Kirk’s arcade)
Figure 2: The course and branches of dorsal pancreatic artery is shown by retracting stomach and body of pancreas. (PAN: pancreas; DUO: duodenum; CT: coeliac trunk; A: aorta; SA: splenic artery; LGA: left gastric artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; DPA: dorsal pancreatic artery; TPA: transverse pancreatic artery; KA: Kirk’s arcade; ASPDA: anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; RGEA: right gastroepiploic artery; SV: splenic vein)
Figure 4: Diagrammatic representation of the present case. (LGA: left gastric artery; SA: splenic artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; DPA: dorsal pancreatic artery; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; PSPDA: posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; ASPDA: anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery; RGEA: right gastroepiploic artery; KA: Kirk’s arcade; IPDA: inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery; FJA: first jejunal artery; TPA: transverse pancreatic artery; SMA: superior mesenteric artery)
Discussion
Knowledge of variations of upper abdominal arteries is important while dealing with gastric and duodenal ulcers, biliary tract surgeries and mobilization of the head of pancreas; since bleeding is one of the complications of these surgeries. According to Michels, when ligation of the common hepatic artery for hepatic arterial aneurysm or portal hypertension is made proximal to the gastroduodenal artery, collateral circulation routed through the Kirk’s arcade may reach the liver for maintenance of life sustaining blood to the organ. Since survival following ligation of hepatic artery is dependent upon the level of the ligation; presence of variant vessels, the extent of development of a true collateral circulation from arteries other than the hepatic, and the efficacy of these arcades needs to be established [4]. During pancreaticoduodenectomies or lymph node resection procedures, ligation of IPDA also requires special attention, because of the high incidence of common trunk formation of the first jejunal and IPDA [5]. Taken into consideration the facts that DPA lies at the vascular junction between coeliac trunk and superior mesenteric artery with variable origin and extent, its major role in pancreatic supply, and Kirk’s arcade is almost consistent feature of it, its efficacy as a collateral pathway needs to be evaluated along with that of the cephalic pancreaticoduodenal arcades in surgeries of pancreas or liver.
References
- Bergman RA, Thompson SA, Afifi AK, Saadeh FA. Compendium of Human Anatomic Variation. Baltimore – Munich, Urban & Schwarzenberg. 1988; 79.
- Kirk E. Untersuchungen über die gröbere end feineretopographische Verteilung der Arterien, Venen uns Ausführungsgänge in der menschlichen Bauchspeicheldrüse. Z Ges Anat. 1931; 94: 822–875. (German)
- Woodburne RT, Olsen LL. The arteries of the pancreas. Anat Rec. 1951; 111: 255–270.
- Michels NA. Collateral arterial pathways to the liver after ligation of the hepatic artery and removal of the celiac axis. Cancer. 1953; 6: 708–724.
- Murakami G, Hirata K, Takamuro T, Mukaiya M, Hata F, Kitagawa S. Vascular anatomy of the pancreatico-duodenal region: A review. J Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Surg. 1999; 6: 55–68.