Possible compression of ulnar nerve by an abnormal muscle originating from the tendon of palmaris longus
Saju Binu Cherian*, Satheesha Nayak B, Nagabhooshana Somayaji
Department of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College (Manipal Campus), International Centre for Health Sciences, Manipal, Karnataka State, India.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Saju Binu Cherian
Senior Grade Lecturer of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College (Manipal Campus), International Centre for Health Sciences, Madhav Nagar, Manipal, Udupi District, Karnataka State, 576 104, India.
Tel: +91 820 2922519
Fax: +91 820 2571905
E-mail: sajubinu@gmail.com
Date of Received: September 22nd, 2008
Date of Accepted: December 28th, 2008
Published Online: January 11th, 2009
© IJAV. 2009; 2: 7–8.
[ft_below_content] =>Keywords
compression, abnormal muscle, ulnar nerve, ulnar artery, hypothenar
Introduction
Palmaris longus muscle is a degenerative muscle of the upper limb. It has a short fleshy belly and a long tendon. The muscle originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus in common with the superficial flexor muscles of the forearm. Its tendon crosses superficial to the flexor retinaculum and enters the hand. In the hand it flattens out to form the palmar aponeurosis. It is supplied by the median nerve and is a weak flexor of the forearm.
Case Report
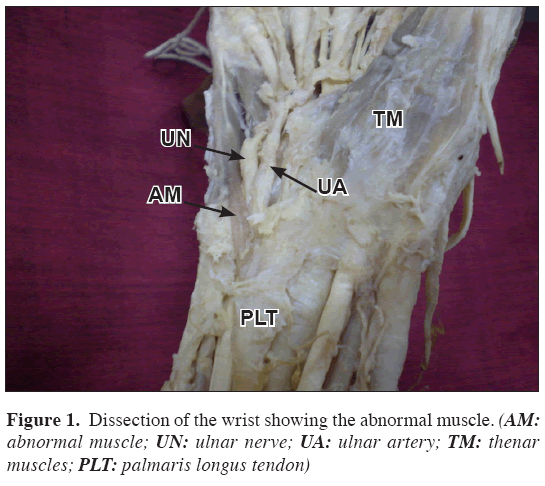
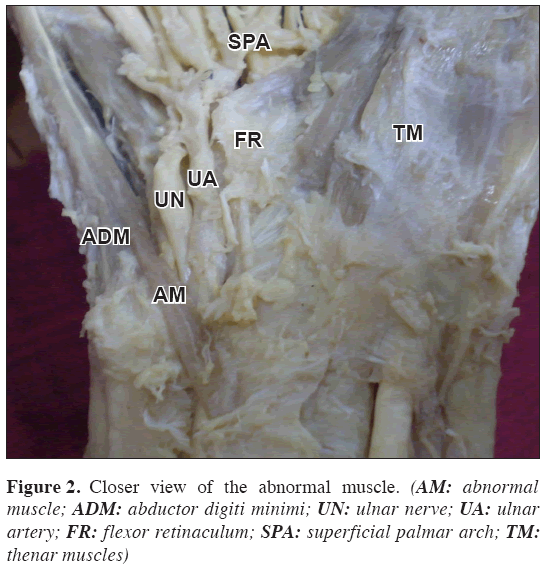
During routine dissections for undergraduate medical students we found an abnormal muscle in the distal part of the forearm. The muscle took its origin from the distal part of the tendon of palmaris longus muscle. It crossed superficial to the ulnar nerve and vessels before they entered the Guyon’s canal (Figures 1, 2). The fleshy belly of the muscle passed superficial to the abductor digiti minimi muscle and became a narrow tendon. The tendon was inserted to the base of the 5th metacarpal bone. The muscle was supplied by a branch of ulnar nerve where it crossed over the nerve.
Discussion
Occurrence of abnormal muscles in the distal forearm and hand is well known. Compression of the ulnar nerve and vessels by such abnormal muscles is also recorded. Luethke and Dellon have reported the compression of ulnar nerve by an accessory abductor digiti minimi muscle [1]. A similar case has also been reported by Al Qattan [2]. Presence of an abnormal muscle in the Guyon’s canal and compression of the ulnar artery has been reported [3]. Palmaris longus muscle shows variations with respect to its fleshy belly and its tendon. Bergman et al., [4] have classified the palmaris longus variations as:
a. complete agenesis,
b. variation in location and form of its fleshy part,
c. aberrancy of attachment at its origin or insertion,
d. duplication and triplication,
e. accessory slips, and
f. replacing elements of a similar form or position.
A three headed reversed palmaris longus muscle has been reported by Natsis et al., [5]. According to the report, such reversed muscle can produce edema of the wrist when it gets hypertrophied. An accessory belly of abductor digiti minimi can arise from the tendon of palmaris longus and pass through Guyon’s canal [6]. It can encircle around the ulnar nerve and vessels and can compress them.
The abnormal muscle that we are reporting is slightly different that the previous reports in the sense that it took origin from the palmaris longus tendon in the distal third of the forearm and it neither passed through the Guyon’s canal nor it passed over it. Instead, it crossed the ulnar nerve and vessels before they entered the Guyon’s canal. The fleshy belly was considerably thick and long. This muscle can compress either ulnar nerve or ulnar artery or both. Having additional muscles like this may not be much useful functionally. The abnormal muscle may be of interest for plastic surgeons and may be of use in muscle transplants.
References
- Luethke R, Dellon AL. Accessory abductor digiti minimi muscle originating proximal to the wrist causing symptomatic ulnar nerve compression. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1992; 28: 307–308.
- Al-Qattan MM. Ulnar nerve compression at the wrist by the accessory abductor digiti minimi muscle: wrist trauma as a precipitating factor. Hand Surg. 2004; 9: 79–82.
- Pribyl C, Moneim MS. Anomalous hand muscle found in the Guyon’s canal at exploration for ulnar artery thrombosis. A case report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994; 306: 120–123.
- Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R. Palmaris Longus. Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Opus I: Muscular System: Alphabetical Listing of Muscles: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/AnatomicVariants/MuscularSystem/Text/P/03Palmaris.shtml (accessed September 2008).
- Natsis K, Levva S, Totlis T, Anastasopoulos N, Paraskevas G. Three-headed reversed palmaris longus muscle and its clinical significance. Ann. Anat. 2007; 189: 97–101.
- Soldado-Carrera F, Vilar-Coromina N, Rodríguez-Baeza A. An accessory belly of the abductor digiti minimi muscle: a case report and embryologic aspects. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2000; 22: 51–54.
Saju Binu Cherian*, Satheesha Nayak B, Nagabhooshana Somayaji
Department of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College (Manipal Campus), International Centre for Health Sciences, Manipal, Karnataka State, India.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Saju Binu Cherian
Senior Grade Lecturer of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College (Manipal Campus), International Centre for Health Sciences, Madhav Nagar, Manipal, Udupi District, Karnataka State, 576 104, India.
Tel: +91 820 2922519
Fax: +91 820 2571905
E-mail: sajubinu@gmail.com
Date of Received: September 22nd, 2008
Date of Accepted: December 28th, 2008
Published Online: January 11th, 2009
© IJAV. 2009; 2: 7–8.
Abstract
Presence of abnormal muscles in the distal forearm and hand is not uncommon. We report an abnormal muscle in the distal part of the forearm and hand. The muscle took its origin from the distal part of the tendon of palmaris longus muscle and crossed superficial to ulnar nerve and vessels. It passed superficial to the hypothenar muscles and got inserted to the base of the fifth metacarpal bone. This abnormal muscle might compress the ulnar nerve, ulnar artery or both.
-Keywords
compression, abnormal muscle, ulnar nerve, ulnar artery, hypothenar
Introduction
Palmaris longus muscle is a degenerative muscle of the upper limb. It has a short fleshy belly and a long tendon. The muscle originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus in common with the superficial flexor muscles of the forearm. Its tendon crosses superficial to the flexor retinaculum and enters the hand. In the hand it flattens out to form the palmar aponeurosis. It is supplied by the median nerve and is a weak flexor of the forearm.
Case Report
During routine dissections for undergraduate medical students we found an abnormal muscle in the distal part of the forearm. The muscle took its origin from the distal part of the tendon of palmaris longus muscle. It crossed superficial to the ulnar nerve and vessels before they entered the Guyon’s canal (Figures 1, 2). The fleshy belly of the muscle passed superficial to the abductor digiti minimi muscle and became a narrow tendon. The tendon was inserted to the base of the 5th metacarpal bone. The muscle was supplied by a branch of ulnar nerve where it crossed over the nerve.
Discussion
Occurrence of abnormal muscles in the distal forearm and hand is well known. Compression of the ulnar nerve and vessels by such abnormal muscles is also recorded. Luethke and Dellon have reported the compression of ulnar nerve by an accessory abductor digiti minimi muscle [1]. A similar case has also been reported by Al Qattan [2]. Presence of an abnormal muscle in the Guyon’s canal and compression of the ulnar artery has been reported [3]. Palmaris longus muscle shows variations with respect to its fleshy belly and its tendon. Bergman et al., [4] have classified the palmaris longus variations as:
a. complete agenesis,
b. variation in location and form of its fleshy part,
c. aberrancy of attachment at its origin or insertion,
d. duplication and triplication,
e. accessory slips, and
f. replacing elements of a similar form or position.
A three headed reversed palmaris longus muscle has been reported by Natsis et al., [5]. According to the report, such reversed muscle can produce edema of the wrist when it gets hypertrophied. An accessory belly of abductor digiti minimi can arise from the tendon of palmaris longus and pass through Guyon’s canal [6]. It can encircle around the ulnar nerve and vessels and can compress them.
The abnormal muscle that we are reporting is slightly different that the previous reports in the sense that it took origin from the palmaris longus tendon in the distal third of the forearm and it neither passed through the Guyon’s canal nor it passed over it. Instead, it crossed the ulnar nerve and vessels before they entered the Guyon’s canal. The fleshy belly was considerably thick and long. This muscle can compress either ulnar nerve or ulnar artery or both. Having additional muscles like this may not be much useful functionally. The abnormal muscle may be of interest for plastic surgeons and may be of use in muscle transplants.
References
- Luethke R, Dellon AL. Accessory abductor digiti minimi muscle originating proximal to the wrist causing symptomatic ulnar nerve compression. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1992; 28: 307–308.
- Al-Qattan MM. Ulnar nerve compression at the wrist by the accessory abductor digiti minimi muscle: wrist trauma as a precipitating factor. Hand Surg. 2004; 9: 79–82.
- Pribyl C, Moneim MS. Anomalous hand muscle found in the Guyon’s canal at exploration for ulnar artery thrombosis. A case report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994; 306: 120–123.
- Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R. Palmaris Longus. Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Opus I: Muscular System: Alphabetical Listing of Muscles: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/AnatomicVariants/MuscularSystem/Text/P/03Palmaris.shtml (accessed September 2008).
- Natsis K, Levva S, Totlis T, Anastasopoulos N, Paraskevas G. Three-headed reversed palmaris longus muscle and its clinical significance. Ann. Anat. 2007; 189: 97–101.
- Soldado-Carrera F, Vilar-Coromina N, Rodríguez-Baeza A. An accessory belly of the abductor digiti minimi muscle: a case report and embryologic aspects. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2000; 22: 51–54.