Psycho-Social Stress Influencing Chronic Temporo-Mandibular Joint Subluxation–A Case Study and Follow-up
2 Department of Psychiatry, Arupadaiveedu Medical College & Hospital, Puducherry, India, Email: dentist123@gmail.com
3 Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, Rajah Muthiah Dental College & Hospital, Annamalai University, Chidambaram, India, Email: dentist123@gmail.com
4 Department of Psychiatry, Pondicherry Institute of Medical Sciences, Kanagachettikulam, Kalapet, Pondicherry, India, Email: dentist123@gmail.com
Received: 01-Dec-2017 Accepted Date: Feb 01, 2018; Published: 09-Feb-2018
Citation: Kannan VS, Elavarasi E, Thivya T, et al. Psycho-Social Stress Influencing Chronic Temporo-Mandibular Joint Subluxation–A Case Study and Follow-up. J Dent and Oral Res 2017;1(1):9-12
This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits reuse, distribution and reproduction of the article, provided that the original work is properly cited and the reuse is restricted to noncommercial purposes. For commercial reuse, contact reprints@pulsus.com
Abstract
Temporo-mandibular Joint (TMJ) Subluxation is defined as the complete loss of articular relationships, between the articular fossa of the temporal bone and the Condylar head, during wide mouth opening. The common etiological factors responsible for TMJ subluxation are traumatic occlusion, occlusal trauma, TMJ ligament & capsule laxity, masticatory muscles disorientation, internal derangement of TMJ and Psycho-social stress. Treatment of TMJ subluxation remains a complex mission. Condylectomy, has been well explained and reported by many authors, which removes the mechanical obstacle, avoids the joint locking, but the TMJ ligament, capsular and masticatory muscles were attached to the condyle will get detached, which in-turn fails to form a healthy pseudo-joint. Here we present a well-documented and in current surgical practice technique of eminectomy, which full fill both in removing the mechanical obstacle and in restoration of healthy Pseudo-TMJ for the patient with severe Subluxation influenced by psycho-social stress.
Keywords
TMJ Subluxation; Psycho-Social stress; Eminectomy
Introduction
Pain of the temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) has been a riddle for a long time, and postulates, hypotheses, and theories abound the literature, but it remains a puzzle, yet to be solved conclusively. Trauma and subsequent changes in the joint and psychological factors that cause strain and spasm of the perioral muscles can cause dysfunction and pain of the TMJ. The complex nature of the TMJ and its dependence on the perioral structures has caused ambiguity in the mechanism, nature, and treatment protocol for Subluxation. Conservative treatment methods, such as medications, exercises, splint, and so forth, are widely accepted as the first line of management. Although pharmacotherapy including analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and tricyclin antidepressant Drugs may help to alleviate the pain and give symptomatic relief to the patient, it does not reverse the dysfunction due to Subluxation. Invasive techniques like open surgery are usually reserved for patients who do not respond to conservative methods. Most of the invasive procedures are not devoid of complications. Here we did Bi-lateral Eminectomy procedure for this patient under GA to remove the mechanical obstruction of head of the condyle
Case Report
A 40 yrs old female patient report to our Dental OPD, Aarupadaiveedu Medical College and Hospital, Puducherry, with a complaint of pain and clicking sound in the jaw joint from 2005 (past 12 years), aggravates while opening and closing the mouth. She has a presenting illness of H/O Periodic locking of jaw while wide opening or yarning but self-reduce by her-self (Frequency – 6 to 8 times a day). Past history of Dislocation for about 5 episodes before 12 years, for which she went to a private hospital with open mouth to reduce it (H/O Extraction of all four 3rd molars) and it became habitual & recurrent and now it became self-reduce by patient it-self. She developed radiating pain to Head, Neck and Shoulders, for which she went to many doctors & various specialities for the same problem but she was treated only by medication. No other relevant past medical history.
She has a personal history of Psycho-Social & Economical stress after Tsunami in 26/12/2004 (Lost her whole property & assets). She was residing at fisherman community with her husband and having no children, having lot of family disputes and financial constraints. On General examination she is Conscious, Oriented, Afebrile, Well-built, no other evidence of systemic findings.
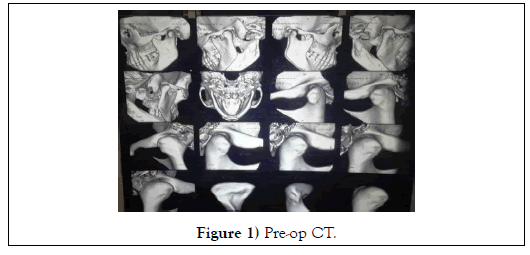
On local examination Face symmetrical, Lip competence, Mouth opening moderate (Inter-Incisal Distance: 30 mm) with slight deviation towards right side. On palpation tenderness and clicking sound present with anterior displacement and slight trapping of head of the Condyle over the Articular Eminence Bi-laterally. CT scan reveals both Condylar head were placed more anterior to the Articular Eminence (Figure 1).
We arrived in to the final diagnosis as Bi-Lateral Temporo-mandibular Joint Subluxation. So, we planned for Bi-lateral Eminectomy under General Anaesthesia and took all necessary investigations for General Anaesthesia, got opinion and clearance from ENT, General Medicine, Psychiatrist, fitness from Anaesthetist and provisionally posted for surgery under General Anaesthesia.
Psychiatric History
Patient has a history of easy irritability, low self-esteem, over expectation from others, difficulty in doing daily activities, bad dreams, suicidal ideas & death wishes on & off, Psychological stresses present due to family disputes and financial constraints, ideas of helplessness and worthlessness, unbelief in god and mood dysthymic, with these history Psychiatrist came to the diagnosis as Psychological depression due to psycho-social stress. They managed the patient with counselling as first line of treatment followed by medication Tablet. Antidep 25mg HS (Anti-depressant); Tablet. Olean 5mg HS (Antipsychotic) for 15 days and advised her to come for review after 15 days postoperatively.
Treatment done
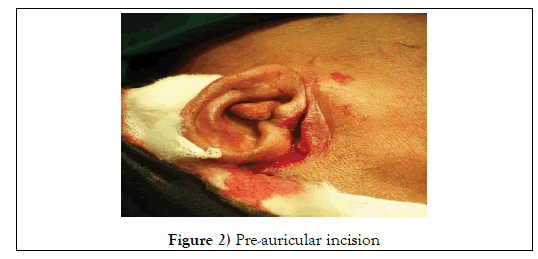
Under Left intubation of ET tube GA was administrated, Bi-lateral Preauricular incision was placed (Figure 2).
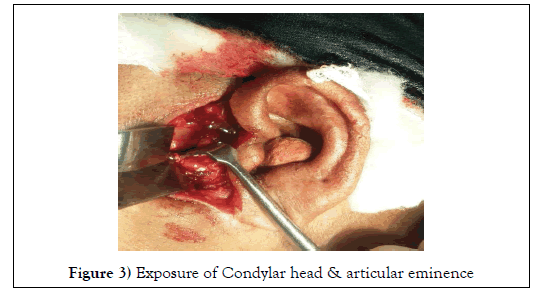
And layer by layer dissection was carried out till superficial deep temporal fascia and incision was placed on fascia at 45o angulation and Zygomatic arch was exposed at the Articular Eminence level (Figure 3).
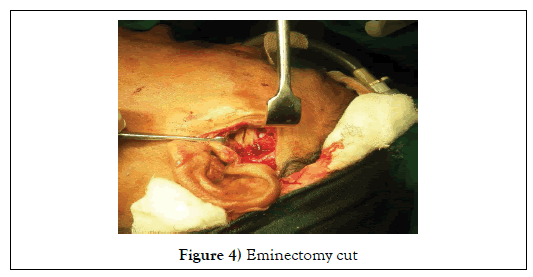
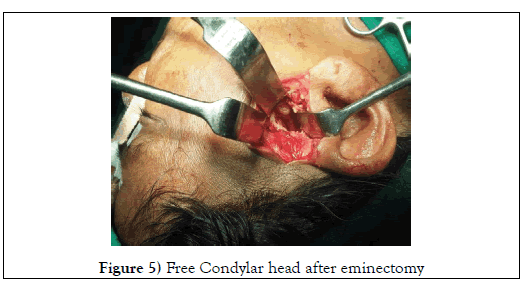
Capsule was pushed in to the upper compartment space and osteotomy cut was made over the eminence using micro-motor, hand-piece and 701 size bur (Figure 4). Eminectomy done using osteotome and mallet, the sharp edges were trimmed using bone trimmer (Figure 5).
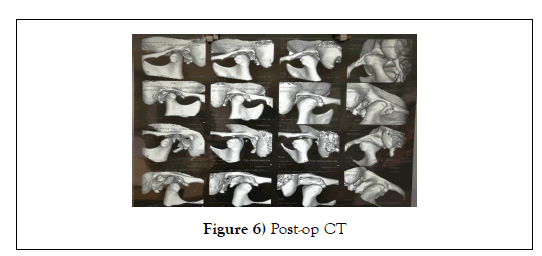
The Capsule was tied over the head of the Condyle, irrigation done using Saline & metrogyl, haemostasis achieved and closure done using 3-0 Vicryl and 4-0 Prolene, Pressure dressing was given. Post-operatively patient was under IV anti-biotics, Analgesics, Proton-Pump Inhibitor for 7 days and Dexamethasone 8mg tapering dose for 3 days, post-op check CT scan was taken (Figure 6).
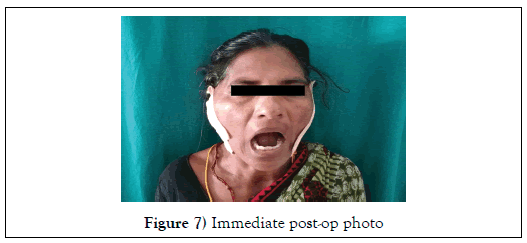
Patient has satisfactory moth opening immediate post-op day without clicking, suture removal done on 7th post-op day (Figure 7).
Follow Up
Regular follow-up was made both in Dental OPD and Psychiatric OPD every 15 days. There is no complication on the operated site and she is devoid of symptoms with acceptable mouth opening without locking or pain, she has stiffness of left TMJ with discomfort while lying down in supine or right lateral position and also she had ulcer in the right lateral border of the tongue with burning sensation due to night bruxism. We did enameloplasty in the right upper & lower posterior teeth over the sharp cusps and prescribed her a xylocaine ointment for topical application and also advised her for TMJ soft occlusal trainer [1], & advised her to wear at least 12 hrs. Per day (Especially during sleeping) patient also referred to Physiotherapy for Infra-red light & TENS therapy for 15 days, in the next visit she had very good prognosis and excellent symptomatic relief.
In Psychiatric OPD she was regularly counselled and continued the same drugs for 5 months, after that she went for psychiatric drug side effect, 2nd degree utero-vaginal prolapse and discontinued the drugs by tapering it .
Discussion
Patho-Physiology of TMJ Subluxation: Temporo-Mandibular Joint (TMJ) is termed as ginglimo-diarthroidal joint since the Articular Disc between the two bony components articular fossa and the head of the Condyle divides the joint space superior-inferiorly into upper and lower compartments [1]. Upper compartment is for ginglimoid movement which permits hinge motion when slight opening of the mouth, Lower compartment is for diarthroidal movement which permits sliding motion when wide opening of the mouth [2]. In open position, the Condylar head moves over the articular eminence and the disk is pulled over the head of the condyle to the posterior convexity of the head of the condyle inferiorly [3]. The posterior bilaminar zone stretches considerably during jaw opening to allow the disc to continue to cover the condyle at all range of motion (preventing friction between the head of the condyle, & articular eminence).
Chronic psychological stress and depression leads to bruxism2 & other form of traumatic occlusion, which in turn reduces the compartment spaces will cause inflammation to superior and inferior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle attached to the pterygoid fovia of condylar head and articular disc respectively, due to that, it causes spasm, fibrous scar, & thus shortening of lateral pterygoid muscle. Which in turn pulls the articular disc posteriorly (absence of stretching of posterior bilaminar zone, thus preventing the disc to cover the condylar head when it moves anteriorly over the articular eminence), causes the two bony components makes friction results in wear and tear of Condylar head and articular eminence [4]. Which results in more anterior displacement and entrapment of condylar head over the articular eminence leads to locking of jaw in open position is termed as “Dislocation”, which should be reduced by the specialist using ‘Naltons Method’, if untreated leads to chronic recurrent dislocation, comes several episodes of frequency a day, which is self-reduced by the patient itself, termed as “Subluxation”.
The first surgical treatment of TMJ Subluxation was introduced in 1883 by Riedel, he did a unilateral Condylectomy. It was followed by Myrhaug in 1951, who stated a procedure eminectomy successfully on two patients 3.
Other invasive techniques for the treatment of subluxation were meniscectomy [4] and closed condylotomy [5,6] Tasanen, et.al, did closed condylotomy using Giggly saw without IMF for treating 21 patients 5.
In 1957, Irby performed the same technique closed condylotomy successfully in thirty cases 6 but due to blind intra-oral approach [7], it may end up with damaging to the TMJ and sometimes fracture of zygomatic arch may occur [8,9].
However, very amazing results have been achieved by eminectomy procedure and its positive progressive outcomes have been proved in many patients with TMJ Subluxation with devoid of intracranial complications. There is a chance for Infection in patients with large marrow space in the articular eminence, which can be avoided by higher antibiotic therapy [10-15].
Blankestijn, et.al, [9] reported a modified eminectomy on 16 patients, osteotomy pertaining to anterior & lateral part of the joint, and then suturing the cartilage with the periosteum covering the osteotomized site. They concluded the success of procedure results from free Condylar movement and post-op fibrous scar formation 9.
Sensoz et al, is the only author compared the height of the articular eminence for treating the 39 patients with Subluxation and underwent bilateral procedure, as the authors believed that TMJ is an inter-dependent joint would eventually become symptomatic even in the presence of unilateral dislocation [16].
Kummoona, used finger like temporalis fascia flap for re-enforcement of capsule laxity and stuffing of crushed cortico-cancellous iliac crest bone in a space anterior to articular eminence was compared with release the fusion of the condyle and capsule from the infratemporal fascia with reverse L-shaped placation and eminectomy and this was supported by animal study on rabbit and founds no cellular changes in the condyle or the surrounding tissue [17].
Medra, et al. concluded that the most successful invasive procedures for the management of TMJ subluxation are that which were performed on the articular eminence. It might be either releasing the mechanical obstacleeminectomy, enhances free condylar movement, or creating a mechanical obstacle to avoid excessive movement of the condyle more anteriorly over the articular eminence. Glenotemporal osteotomy with interpositional bone grafting introduced by Norman’s and on lay bone graft or incomplete down fracture of Zygomatic ach anterior to articular eminence creating an obstacle to condyle termed as Dauterey’s procedure [18].
Sadesh.V.Kannan, stated a new minimally invasive technique ‘Pterygoid Dysjunction’for the management of painful TMJ dysfunction. When the pterygoid plates are fractured and disjoined from the maxilla and the sphenoid base and pushed posteriorly, the pterygoid muscles pull the plates backward and inferiorly. As a result, both muscles, especially the fibers attached to the pterygoid plates, are shortened. This will reduce the spasm and strain on both the pterygoid muscles, reduce the protractile force on the condyle, reduce the upward pull on the condyle [19], and increase the joint space. Because both the upward and anterior pulls on the condyle are reduced (by shortening the pterygoid muscles), the pressure on the posterior bilaminar tissue (which wedges between the condyle and the posterior slope of the articular eminence in the internal derangement) is reduced, resulting in relief of pain. Because the anterior pull on the disk condyle complex is reduced, there is a better chance for the marginally displaced disk to go back to its normal position because of the possible increase in joint space.
Ishank Singhal et.al, Patient`s psychological stress can be the one of the causative factor for TMJ subluxation [20].
Conclusion
It is quiet confusing for the author to come to the definitive conclusion whether the TMJ Subluxation arises due to psycho-social stress or because of TMJ Subluxation, the psycho-social stress arises, but reviewing the past history of the patient that her problem started after the disaster of Tsunami in December, 2004, So we can conclude that Psycho-social stress is the primary cause for TMJ Subluxation.
This case is a chronic case of TMJ Subluxation for past 12 years, TMJ pain (Physical) is clumped with Psychological, Social, Economical, and even Spiritual pain, which in turn termed as “Total Pain” coined by ‘Dame Cicely’ [21], which is very difficult to achieve good prognosis if treated only for TMJ subluxation. So multi-disciplinary approach with psychiatrist, clinical psychologist for counseling, nurses, physiotherapist and family members/ social workers will help to alleviate the symptoms hopefully [22]. Our patient is alleviate of TMJ pain, free of symptoms, & now she is doing all her house hold works and also going for daily work outside. She is coming for regular follow-up and review every 3 months in both Dental OPD & Psychiatric Rejuvenation Clinic regularly.
Acknowledgement
1. Dr. A.S.Ganesan, Hon’ble Chancellor, Vinayaga Mission Research Foundation, Salem.
2. Dr. Anuradha Ganesan, Director, Vinayaga Mission Research Foundation, Salem.
Details of Contributors
All authors contributed to the conception of the work; EDE and AO to the acquisition of data, BWM to the analysis of data, CVEP to the interpretation of data for the work.
BWM and EDE drafted the manuscript; CVEP and AO revised it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript submitted for publication.
Funding
None.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval for the original data collection was granted by the South East Wales Local Research Ethics Committee.
REFERENCES
- Solberg WK, Clark GT, Rugh JD. Nocturnal electromyographic evaluation of bruxism patients undergoing short term splint therapy. J Oral Rehabil 1975;2:215-223.
- Wieckiewicz M, Paradowska-Stolarz A, Wieckiewicz W. Psychosocial aspects of bruxism: The most paramount factor influencing teeth grinding. BioMed Res Int 2014.
- Myrhaug H. A new method of operation for habitual dislocation of the mandible—Review of former methods of treatment. Acta Odontol Scand 1951;9:247-261.
- Dingman RO, Moorman WC. Meniscectomy in the treatment of lesions of the temporomandibular joint. J Oral Surg 1951;9:214.
- Ward TG. Surgery of the mandibular joint. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 1961;28:139-152.
- Tasanen A, Lamberg MA. Closed condylotomy in the treatment of recurrent dislocation of the mandibualr condyle. Int J Oral Surg 1978;7:1-6.
- Irby WB. Surgical correction of chronic dislocation of the TMJ not responsive to conservative therapy. J Oral Surg 1957;15:307-312.
- Schade GJ. Surgical treatment of the habitual luxation of the temporomandibular joint. J Maxillofac Surg 1977;5:146-150.
- Blankestijn J, Boering G. Myrhaug's operation for treating recurrent dislocation of the temporomandibular joint. Cranio 1985;3:245- 250.
- van der Kwast WA. Surgical management of the habitual luxation of the mandible. Int J Oral Surg 1978;7:329-332.
- Lewis JES. A simple technique for long-standing dislocation of the mandible. Br J Oral Surg 1981;19:52-56.
- Cherry CQ, Frew AL. Bilateral reductions of articular eminence for chronic dislocation: Review of 8 cases. J Oral Surg 1977;35:598-600.
- Sanders B, Frey N, McReynolds J. Anatomical, radiographic, and clinical evaluation of temporomandibular articular eminence reduction as a treatment recurrent dislocation and chronic subluxation. Ann Dent 1978;37:33-44.
- Lovely FW, Copeland RA. Reduction eminoplasty for chronic recurrent luxation of the temporomandibualr joint. J Can Dent Assoc 1981;47:179-184.
- Helman J, Laufer D, Minkov B, et al. Eminectomy as surgical treatment for chronic mandibular dislocations. Int J Oral Surg 1984;13:486-489.
- Sensoz O, Ustuner ET, Celebioglu S, et al. Eminectomy for the treatment of chronic subluxation and recurrent dislocation of the temporomandibular joint and a new method of patient evaluation. Ann Plast Surg 1992;29:299-302.
- Kummoona R. Surgical managements of subluxation and dislocation of the temporomandibular joint: Clinical and experimental studies. J Craniofac Surg 2010; 21:1692-1697.
- Medra AM. Glenotemporal osteotomy and bone grafting in the management of chronic recurrent dislocation and hypermobility of the temporomandibular Joint. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2008;46:119-122.
- Sadesh VK. Pterygoid dysjunction: A minimally invasive technique for the treatment of painful TMJ dysfunction. J Craniofac Surg 2010;21.
- Ishank S, Pradkhshana V, Harvey T, et al. Unilateral mandibular dislocation - can patient’s psychology be a contributing factor? A case report. Int J Adv Health Sci 2015;1:14-16.
- Saunders, Dame CM. The management of terminal malignant disease. 1st ed. London: Edward Arnold; 1978.
- Syrjalak K, Chapka M. Evidence of a bio-psychosocial model of cancer-related pain. Pain 1995;61:69–79.