Addiction Science 2019 & Dementia Care 2019
July 24-25, 2019
Page 16
DEMENTIA AND DEMENTIA CARE
ADVANCES IN ADDICTION SCIENCE AND MEDICINE
July 24-25, 2019 | Rome, Italy
10
th
International Conference on
2
nd
World Congress on
&
Volume 2
Journal of Clinical Psychiatry and Neuroscience
Gambling: The hidden disorder
Statement of the Problem
: Gambling is common in Australian society – nearly 75 per cent of Australian adults gamble in
any year. About 300,000 Australians have a gambling problem, but only 10 per cent of people with problematic gambling
behaviour seek help. The hidden nature of gambling disorder has the minimal signs and symptoms concealing the level of
severity associated with this condition subsequently causing significant dysfunction for individuals, and families.
Findings
: Current research recognises that the course of the disorder can vary by type of gambling as well as life
circumstances, and acknowledges the overwhelming evidence indicating its association with consistently high rates of
comorbid psychopathology-particularly mood, anxiety, and substance use disorders; other impulse control disorders;
bipolar disorder; and antisocial personality disorder. For instance, a meta-analysis of 11 population surveys found high
mean prevalence for nicotine dependence (60.1%), a substance use disorder (57.5%), depressive disorders (37.9%), and
anxiety disorders (37.4%).
Theoretical Orientation
: As the largest Victorian service, Gambler’s
Help Southern (GHS) offers a range of evidence-based psychotherapeutic
interventions often individually tailored and underpinned by Cognitive-
Behaviour Therapy (CBT), minimal or brief interventions, Motivational
Enhancement Therapies (MET), mindfulness-based therapies, group and
couple therapies. Newly created interactive online video psychological
interventions and prevention programs will be made available to individuals
with problematic gambling behaviour, and families who are mostly new to
treatment. Financial counselling delivers a range of interventions integrated
with therapeutic and other services. GHS assists close to 2,000 people across Melbourne southern catchments per annum.
Conclusion
: While psychological treatment approaches and interventions are essential to manage tertiary prevention
of gambling, influencing public policy changes are equally necessary, supporting a range of strategies from prevention,
health promotion and treatment, at individual, community, industry and government levels.
Biography
Jasminka Vuckovic-Kosanovic is the Clinical Manager of the Gambler’s Help program, at Connect Health and Community, in Melbourne,
Australia. She hasmade a significant contribution to community services in particular, designing and implementing early intervention programs
in youth mental health and homelessness embedding trauma-informed care into clinical practice and service design. Her extensive clinical
management experience in the community health sector has been brought to bear on clinical complexities of cognitive disability associated
with acquired brain injury, childhood trauma and co-occurring gambling, mental health and other addictive disorders. She has implemented
interactive online video psychological interventions and prevention programs for individuals with problematic gambling behaviour and families
who are mostly new to treatment. She has a Masters of Global Health and Social Work, with her main interest in co-occurring mental health
and addictive disorders, has prepared a number of paper presentations, and peer-reviewed articles on these topics.
j.kosanovic@connecthealth.org.auJasminka Vuckovic-Kosanovic
Gambler’s Help Services, Australia
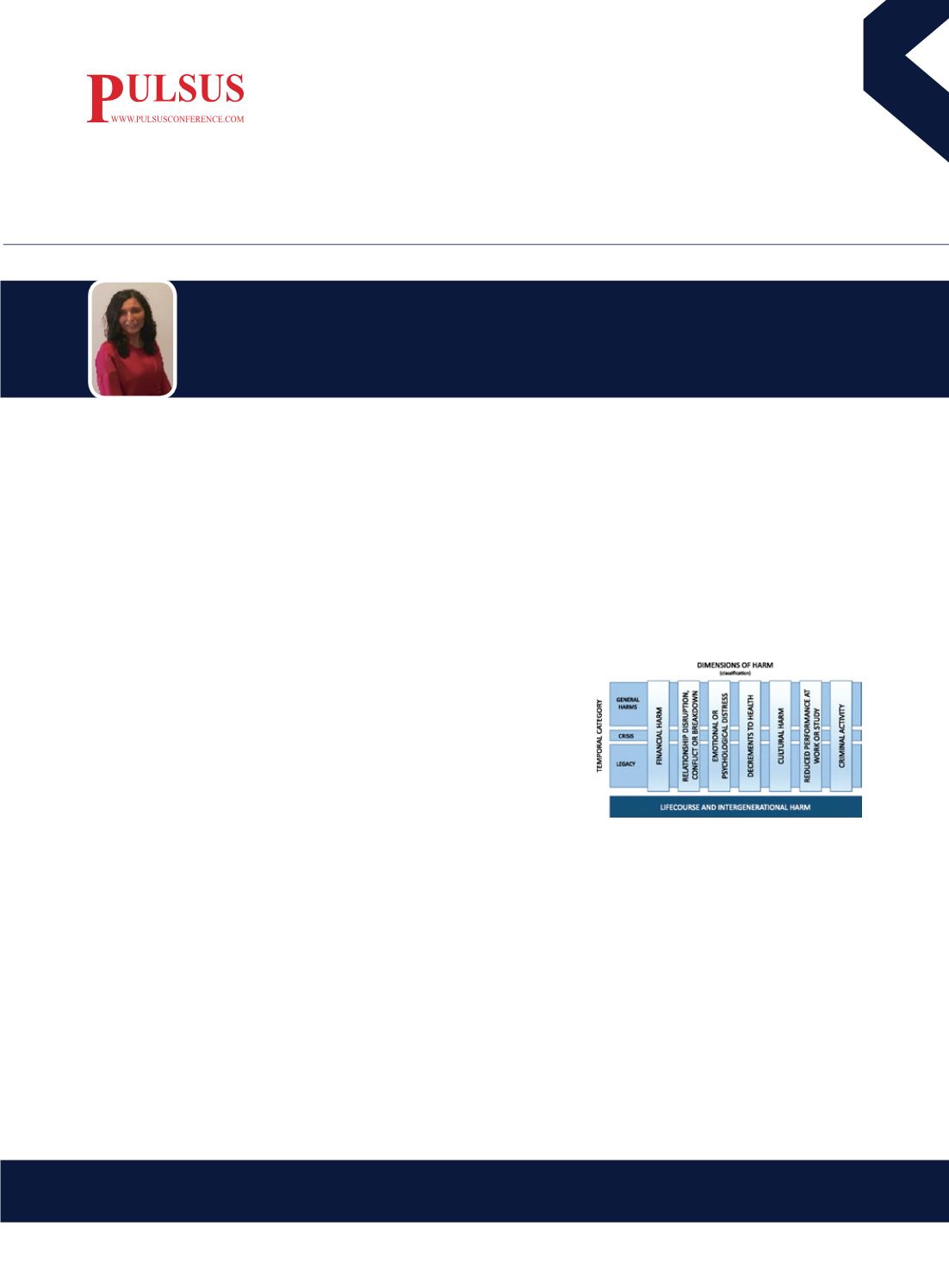
Figure1: Conceptual Framework of Gambling Related Harm
J Clin Psychiatr Neurosci, Volume 2