Page 24
Notes:
Volume 2
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology Reports
Microbial Biotechnology 2018
September 17-18, 2018
Microbial Biotechnology & Vaccine Design
September 17-18, 2018 Lisbon, Portugal
5
th
World Congress on
Evaluation of antimicrobial peptides in fermented breast milk
Diana Martinez and Enrique Maldonado Cervantes
Autonomous University of San Luis Potosí, Mexico
Introduction & Aim:
The antibiotic resistance is a world problem due to genetic modification of microorganisms rendering them
ineffective. This increases the spread of infections in the population and it has become an alarming public health problem. A promising
solution to solve this problem is the use of antimicrobial peptides obtained from natural sources such as Breast Milk (BM), therefore
the aim of this investigation is to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of peptides obtained from the fermentation of BM using probiotic
bacteria found in the same one.
Methodology:
Three samples of BM was pasteurized and inoculated with
Bifidobacterium
spp.,
Lactobacillus
spp., and
Streptococcus
spp. genera which were isolated from BM through selective mediums and incubated at 37 °C under anaerobic conditions for 37
hours. The whey proteins amount was determined by Bradford method. The whey proteins were visualized in acrylamide gel at
16% concentration. The separation of whey proteins was done by size exclusion chromatography with Poly (allyl dextran]-co-
N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide) within 25-75 microns resin and it was quantified with the Bradford method and visualized in SDS-
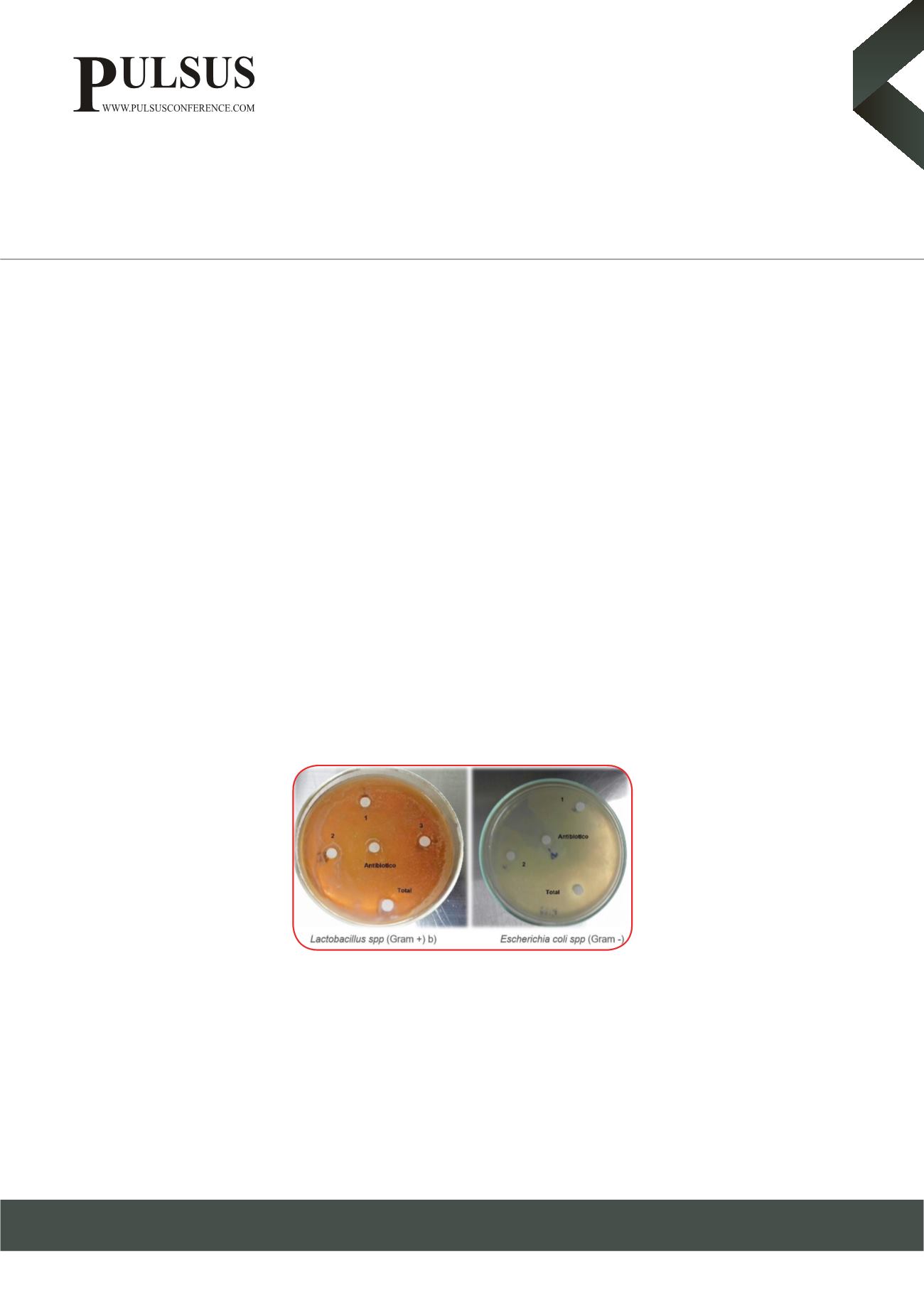
PAGE. The antimicrobial characteristics of the protein fractions were evaluated on Gram negative and positive bacteria using disks
impregnated of whey protein fractions.
Findings:
The fermentation of milk stopped at the exponential phase of bacterial growth. The range of weight of whey proteins was
10-75 kDa and a significant low weight proteins concentration. In all cases, four fractions were obtained in the chromatography
separation, nevertheless only one contained proteins lower than 10 kDa. The antibiogram assay determinedmicrobiological inhibition
of whey proteins in both the Gram-positive and negative bacterial genera.
Conclusion & Significance:
It was confirmed the proteolitical activity of probiotics genera on BM and the consequent liberation of
broad spectrum antimicrobial peptides.
Biography
Diana Martinez is a PhD student in the Autonomous University of San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Her research interest is in antimicrobial peptides, bacterial studies, etc.
She is working under Professor Enrique Maldonado at the UASLP in Mexico.
96diana@live.com.mxDiana Martinez et al., J Microbio and Biotech Rept 2018, Volume 2