Page 13
August 5-6, 2019 | Singapore
Volume 3
Cancer Research 2019 & Structural Biochemistry 2019
August 5-6, 2019
Journal of Cancer and Metastasis Research
CANCER RESEARCH AND PHARMACOLOGY
STRUCTURAL BIOCHEMISTRY, STEM CELLS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
24
th
International Conference on
International Congress on
&
Clin Psychol Cog Sci, Volume 3
Noninvasive risk stratification of patients using predictive biomarker apoptosis index
of tumors
Statement of the Problem
: Human tumors are heterogeneous which evoke different responses from different treatments.
Current animal models used in cancer research are xenografts which
would not mimic human tumors. A noninvasive imaging modality to
assess cell death in target and non-target organs simultaneously may
help to overcome the heterogeneity and may identify a biomarker
which can be used to predict the efficacy and toxicity of treatments.
Apoptosis Index (AI) is the measure of cell death in tumor, the
modulation of which reflects how it responds to therapy. For example,
we and others have shown that lower the spontaneous AI, lower the
response and vice versa from the treatments irrespective of the nature
of treatments. We have developed a novel technology “A Priori
Activation of Apoptosis Pathways of Tumor” (AAAPT) which raises
AI of spontaneous tumors above a threshold level in order to evoke a
better response from therapy.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation
: Cancer cells have
ability to enhance survival pathways (e.g. NF-kB and PARP) and down regulate the cell death pathways (e.g. CD95,
ASK1) for their survival. Hence, we have designed new technology to target these pathways to sensitize those resistant
tumor cells using targeted activation technology. We have used clinically oriented SPECT and Ultrasound Imaging
techniques to assess AI as a predictive biomarker of efficacy and toxicity of chemotherapy respectively.
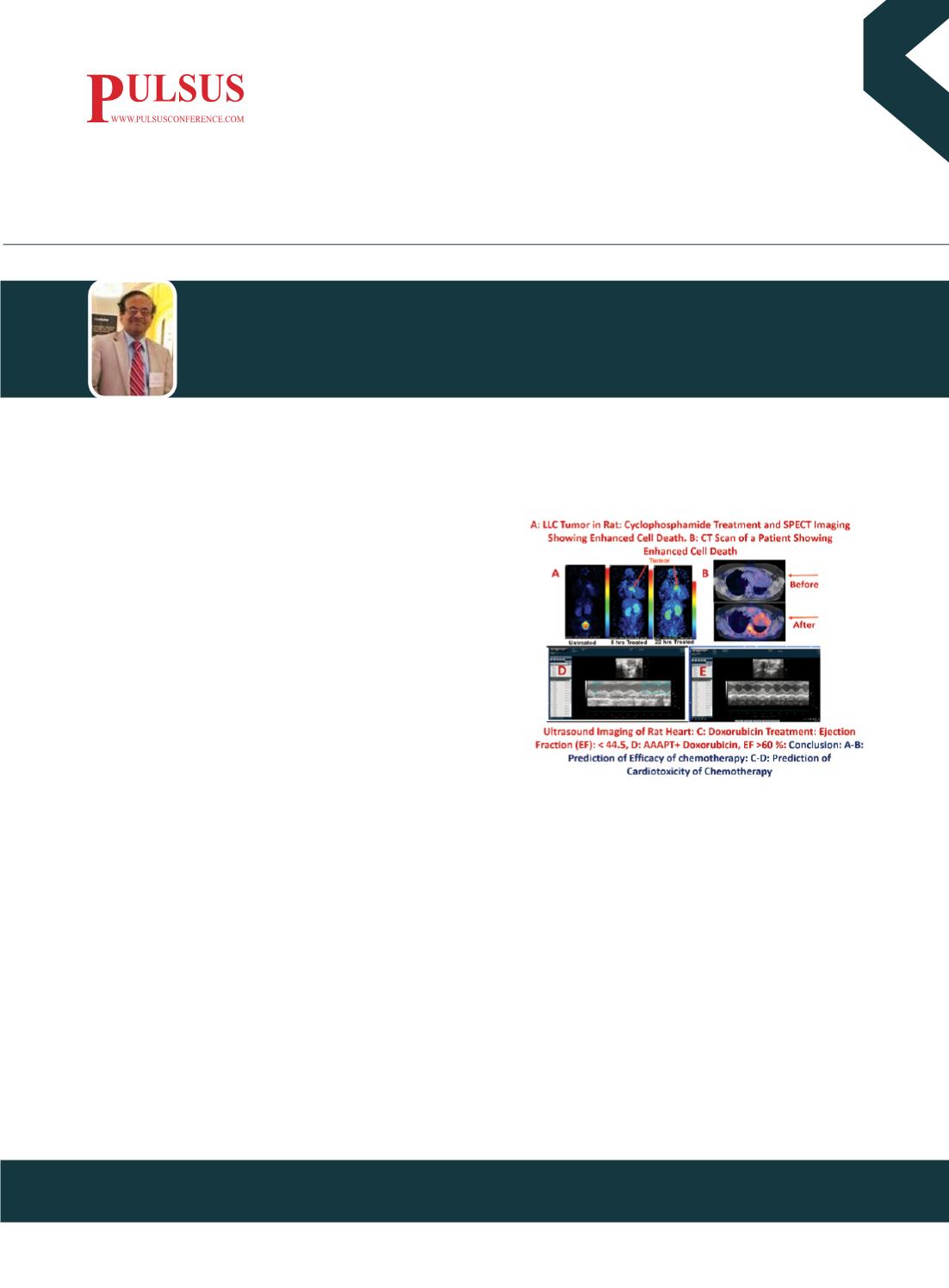
Findings
: SPECT imaging of Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) showed an enhanced cell death (higher AI) post treatment
by Cyclophosphamide while, US imaging reversed the cardiotoxicity by doxorubicin by using AAAPT as a neoadjuvant
to Doxorubicin.
Conclusion & Significance
: The noninvasive assessment of AI (measure of cell death) by SPECT combined with
US imaging can be used to risk stratify patients in terms of who responds to which therapy earlier compared to tumor
regression timelines.
Biography
Raghu Pandurangi started his scientific career Ph.D in spectroscopy followed by post-doctoral training at Radiology and Internal medicine,
University of Missouri, Columbia where he remained as a faculty for 10 years. He was a principle investigator position in Shering AG, Ger-
many where he directed and involved in 2 FDA approved drugs (AccuTect and NeoTect). He was a team leader at Mallinckrodt directing
apoptosis imaging. He became an entrepreneur in 2013 inventing AAAPT technology for improving FDA approved drugs. Currently, he is the
Founder, President and CSO of Sci-Engi-Medco Solutions (SEMCO) and Amplexi-LLC, recipient of several NIH grants and awards.
raghuaa66@yahoo.comRaghu Pandurangi
Sci-Engi-Medco SolutionsInc, USA