Page 14
August 5-6, 2019 | Singapore
Volume 3
Cancer Research 2019 & Structural Biochemistry 2019
August 5-6, 2019
Journal of Cancer and Metastasis Research
CANCER RESEARCH AND PHARMACOLOGY
STRUCTURAL BIOCHEMISTRY, STEM CELLS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
24
th
International Conference on
International Congress on
&
Hydrogen peroxide inducible clone-5 mediates positive feedback ROS-JNK-c-jun
signaling for HCC progression
T
he poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is due to
high recurrence rate mainly caused by intrahepatic metastasis.
Hic-5 (hydrogen peroxide inducible clone-5) which belongs to the
paxillin superfamily can be stimulated by a lot of metastatic factors
including transforming growth factor (TGF
β
) and hepatocyte growth
factor (HGF), which further regulate epithelial mesenchymal transition
(EMT), migration and invasion. The molecular mechanisms for Hic-5
to trigger EMT and tumor progression appeared to be closely associated
with its impact on signal transduction. Our recent report demonstrated
that Hic-5 not only can be a poor prognosis marker for HCC but also
served as a mediator of the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-c-jun-N-
terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway for HCC progression. Notably,
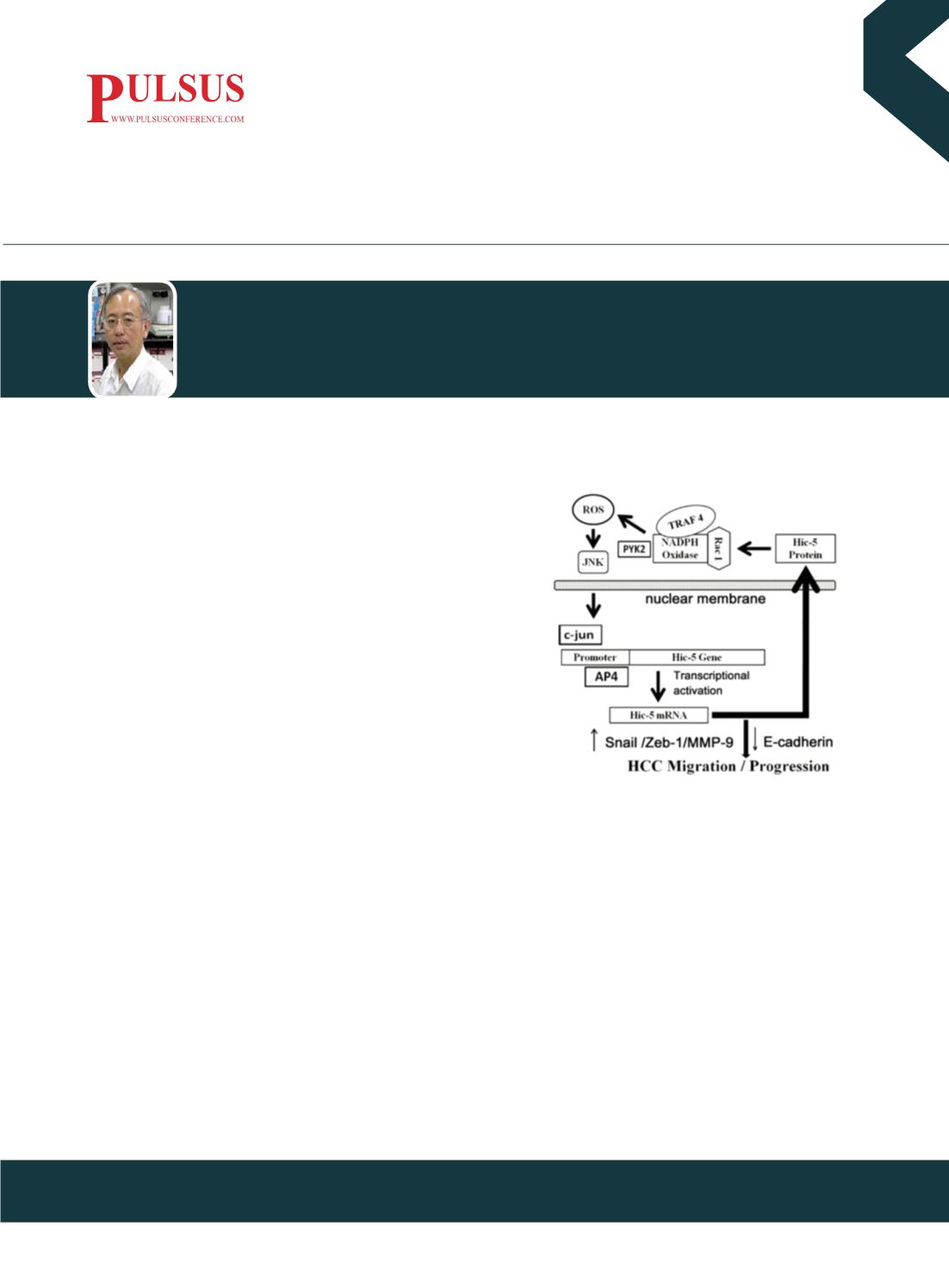
Hic-5 appeared to locate both upstream and downstream of ROS-JNK
cascade. In our recent study, a more comprehensive Hic-5-ROS-JNK
positive feedback pathway has been established. Specifically, Hic-5 may
interact with regulators of NADPH oxidase such as Rac-1, Traf4 and
nonreceptor tyrosine kinase (Pyk2) for activating NADPH oxidase and
ROS generation, leading to JNK phosphorylation and transcriptional
activation of Hic-5 mediated by c-jun/AP-4. The Hic-5 thus induced in
turn re-activates the ROS-JNK signal cascade. This positive feedback
circuit is essential for elevating mesenchymal transcriptional factors
such as Snail, Zeb1 and matrix degradation enzyme MMP9 and decreasing the epithelial marker E-cadherin (Fig.1).
Currently, the missing links in both the upstream and downstream of Hic-5-NADPH oxidase-ROS-JNK-c-jun pathway are
being clarified. Moreover, whether knockdown of Hic-5
in vivo
may decrease HCC progression in a SCID mice are being
investigated. Our study will benefit designing a more effective target therapy aiming at Hic-5 against HCC.
Biography
Wen-Sheng Wu graduated from institute of biochemistry Taiwan University getting PhD degree on 1988. He carried postdoctoral research
at department of research, veteran general hospital Taipei and department of Medical technology Kaohsiung, Taiwan. He is now a professor
in Department of laboratory medicine and biotechnology, college of Medicine, Tzu Chi University. His research interest are. Signaling and
transcriptional mechanisms for tumor progression and Target therapy against cancer.
wuws@gms.tcu.edu.twWen-Sheng Wu
Tzu Chi University, Taiwan
Figure 1. Hic-5 mediated positive feedback NADPH oxidase- ROS-
JNK-c-jun cascade, regulating EMT markers. Hic-5 transcription can
be induced by ROS-JNK-c-jun pathway which may in turn interact
with Rac1 and Traf4, triggering activation of NADPH oxidase, ROS
generation and JNK phosphorylation thus sustaining the signal
transduction. The positive feedback Hic-5-ROS-JNK signaling circuit
further upregulates Snail, Zeb-1 and MMP-9 and downregulate
E-cadherin for triggering HCC migration and progression of HCC