Volume 3
Journal of Neurology and Clinical Neuroscience
Neurology 2019 | Neuropsychology 2019 | Drug Delivery Summit 2019
June 24-25, 2019
Page 21
June 24-25, 2019 | Rome, Italy
Neurology and Healthcare
3
rd
WorldDrug Delivery and Formulations Summit
Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology
4
th
International Conference on
International Conference on
&
Lalit Garg
University of Malta, Malta
Application of machine learning and signal processing techniques to real time detection and prediction
of epileptic seizures
E
pilepsy is a neurological disease, which affects around 50 million people of the world’s population and 25%
of them have medically resistant form of epilepsy. With the increased development of effective prevention
treatments, early diagnosis of epileptic seizures is becoming necessary because the patient can undergo treatments,
which can delay or prevent the disease progression. Several studies have been carried out in the past to explore the
feasibility of a practical real-time epilepsy seizure detector. However, still there is a need for improved methods of
data acquisition, feature extraction and feature space creation for epilepsy seizure detection. Also, there is no known
technique available for accurately predict a seizure onset well ahead. An accurate prediction even fewminutes before
the seizure onset might help prepare the patient, his/her caregiver. This talk will present the energy efficient real-time
seizure detection and prediction algorithms we developed [1-5], which can be implemented in wearable, non-invasive
EEG devices which would ensure prompt and effective management of seizures. The research focus also includes
development of accurate seizure detection and prediction algorithms to prevent or minimize harmful effects of seizure
onsets. Our methods [1-5] differ from previous studies mainly on two things; the first is providing a simple yet very
effective training set acquisition for epileptic seizure detection and prediction, and the second is testing these novel
approaches using a high number of seizure instances, precisely a total of 192 seizures from total 22 pediatric patients.
Biography
Lalit Garg is a Lecturer in Computer Information Systems at the University of Malta, Malta. He is also an honorary lecturer at the University
of Liverpool, UK. He has also worked as a researcher at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore and at the University of Ulster,
UK. He received his first degree in electronics and communication engineering from the Barkatullah University, Bhopal, India, in 1999 and his
postgraduate in information technology from the ABV-Indian Institute of Information Technology and Management (IIITM), Gwalior, India in
2001. He received his Ph.D. degree from the University of Ulster, Coleraine, UK., in 2010. His research interests are missing data handling,
machine learning, data mining, mathematical and stochastic modelling and operational research, and their applications especially in the
healthcare domain. He has published over 80 technical papers in refereed high impact journals, conferences and books and has more than
550 citation count to his publications.
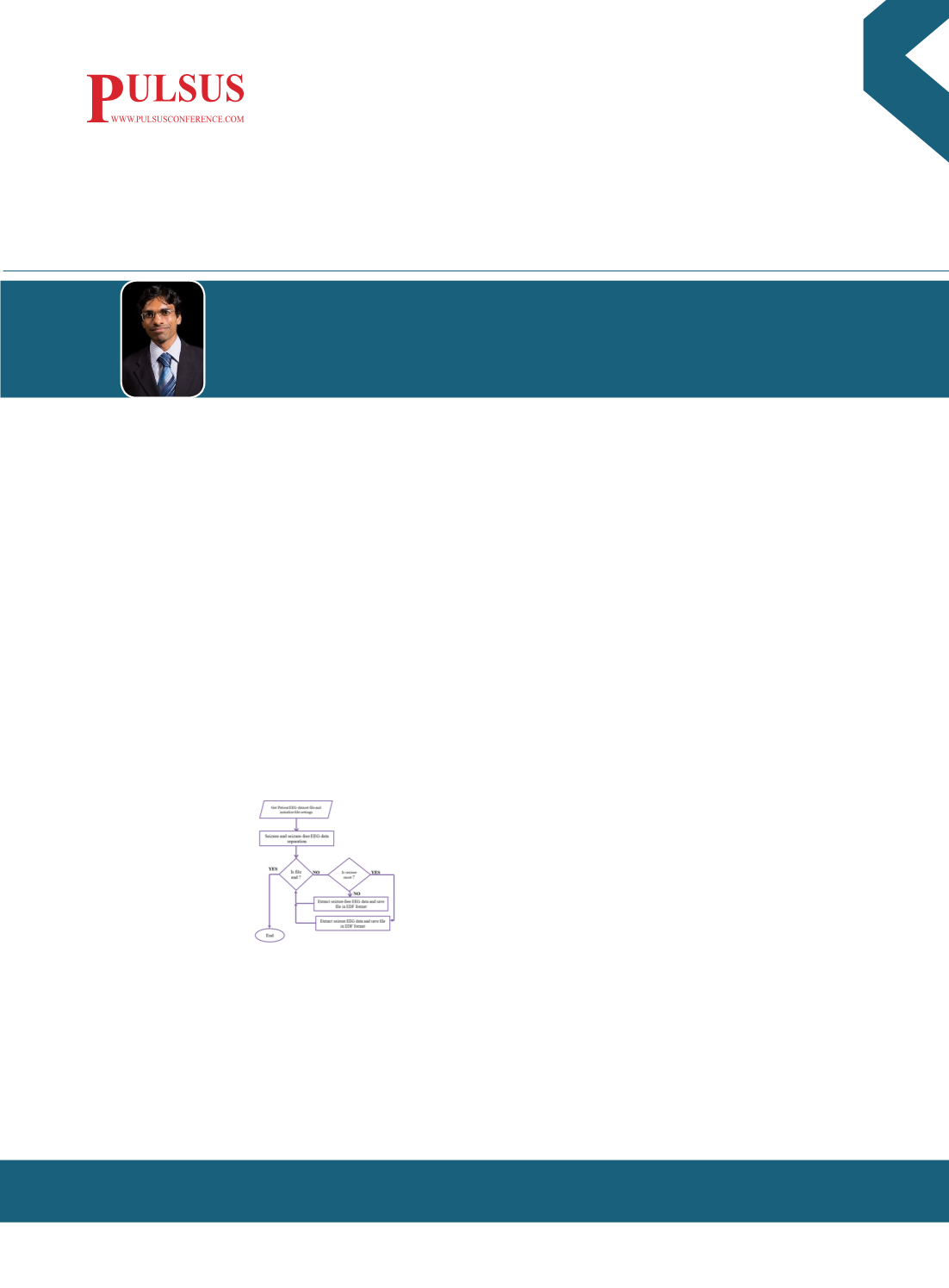
lalit.garg@um.edu.mtFigure1: Pre-processing of scalp EEG data into separate seizure and
seizure free EEG files
J Neurol Clin Neurosci, Volume 3