Page 21
Notes:
Volume 1, Issue 1
J Nurs Res Pract
Nursing Care & Breast Congress 2017
December 11-13, 2017
December 11-13, 2017 | Rome, Italy
Joint Event
&
45
th
WORLD CONGRESS ON NURSING CARE
8
TH
EUROPEAN BREAST CONGRESS
The door to the inner world of children in nursing care: Drawing and writing technique
Cigdem Sari
Gazi University, Turkey
A
rt is a versatile skill that nature presents. Art is the work of people who can think, see the truth, and understand society.
When taking consideration of these characteristics, the nursing care overlaps with this view. The precondition of the
realization of the stages of planning, implementation, and evaluation of nursing care is to understand the individual and touch
his/her world. Care is "art", "touching the soul", "hearing the life". This situation becomes more important when children who
develop differently at each age period are concerned. It is important to use therapeutic communication techniques appropriate
to age characteristics of children in order to access their world and understand them in the protection and development of
their health and in case of an illness. One technique that allows the child to express his/her feelings non-verbally and in an
artistic way is drawing pictures and then writing what is drawn. The technique of drawing and writing about it by narrating
is a therapeutic communication technique that can be used to visualize and express the vital events that affect the child, the
disease process and how he perceives himself/herself. The picture's narrative qualities are the ability of children to present their
own inner worlds, their developmentally appropriate form of communication, and presenting their personal stories by talking
to an expert about the content of the picture. There are important clues that enable us to access children's inner world and will
be used for evaluation. The size, order, and settlements of shapes, proportions, colors, usage area of paper, and lines in his/her
paintings and their personal interpretation of the pictures they drew provide important information in evaluating children's
pictures. Children can think and imagine that goes beyond their drawings. For this reason, drawing pictures-with the writing
technique allows us to reach children more. In this sense, considering the literature, it’s seen that drawing technique is often
used both in healthy children and also during the studies of the effects of an illness or vital events (migration, war etc.) on
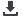
children. However, the studies in which the drawing and writing technique are used together are limited. Figure 1 shows a
picture of a 13-year-old girl with diagnosis of ALL drawn according to the Directive of Hospitalized child. In the story of the
picture, it’s stated that a girl who is given blood in the hospital draws the food she misses and cannot eat with her family in a
picnic. It is recommended that children's nurses should be trained in therapeutic communication techniques so that they can
use pictures which are a projective technique. They can be trained with post-graduate professional courses to understand and
interpret children's pictures and can give direction to their care system in the clinical environment. They can perform their
professional roles like a caregiver, educator and advocate with effective care.
Biography
Cigdem Sari Gazi University Health Sciences Faculty Nursing Department, Ankara, Turkey Sari completed nursing bachelor program in Fırat University, School of
Nursing in 2012, and graduated ranking first in the nursing department. Sari completed master degree in Gazi University School of Nursing in 2014 and has started
the doctorate program in 2014 and ongoing her research. Sari became a research assistant in Gazi University Health Sciences Faculty in 2012, and her tenure still
in progress in the same position. At the same time, She has been a lactation consultant.
cigdemsarii@hotmail.comCigdem Sari, J Nurs Res Pract 2017, 1:1(Suppl)