Journal of Pediatric Health Care and Medicine Volume 1, Issue 1
Page 10
http://pediatrics.cmesociety.comSeptember 11-12, 2017 Los Angeles, CA, USA
14
th
World Pediatrics &
Neonatal Healthcare Conference
Pediatrics & Neonatal Healthcare 2017
Introduction and maintenance of early adaptive training protein blends in support of
infant nutritional goals: Safety and acceptability
C
hildhood food allergy affects about 8% of US children. Recent research has revealed protective effects of
early dietary introduction of allergenic foods on the development of food allergy for infants, including those
at elevated risk. The goal of this study was to evaluate the safety and acceptability of a blend of 16 common
allergenic proteins (peanut, soy, almond, cashew, hazelnut, pecan, pistachio, walnut, wheat, oat, milk, egg, cod,
shrimp, salmon, and sesame) combined with 400 IU of Vitamin D into a food supplement powder. Caregivers
were instructed to mix the powder into a solid or liquid feeding once a day. All procedures were deemed exempt
by the Northwestern University IRB. A national sample of healthy infants, 5-11 months of age, without severe
eczema participated in the 28-day placebo period followed by a 28-day randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled
period. Caregivers were instructed to feed the infant one packet of the food supplement powder per day, observe
their infant for 2 hours after ingestion, and record, in a web-based diary, any symptoms or allergic-type reaction
including anaphylaxis occurring within 2 hours of ingestion and any reaction-related prescribed medication or
medical care. Caregiver perceptions of the food supplement’s smell, texture, and packaging, were also assessed.
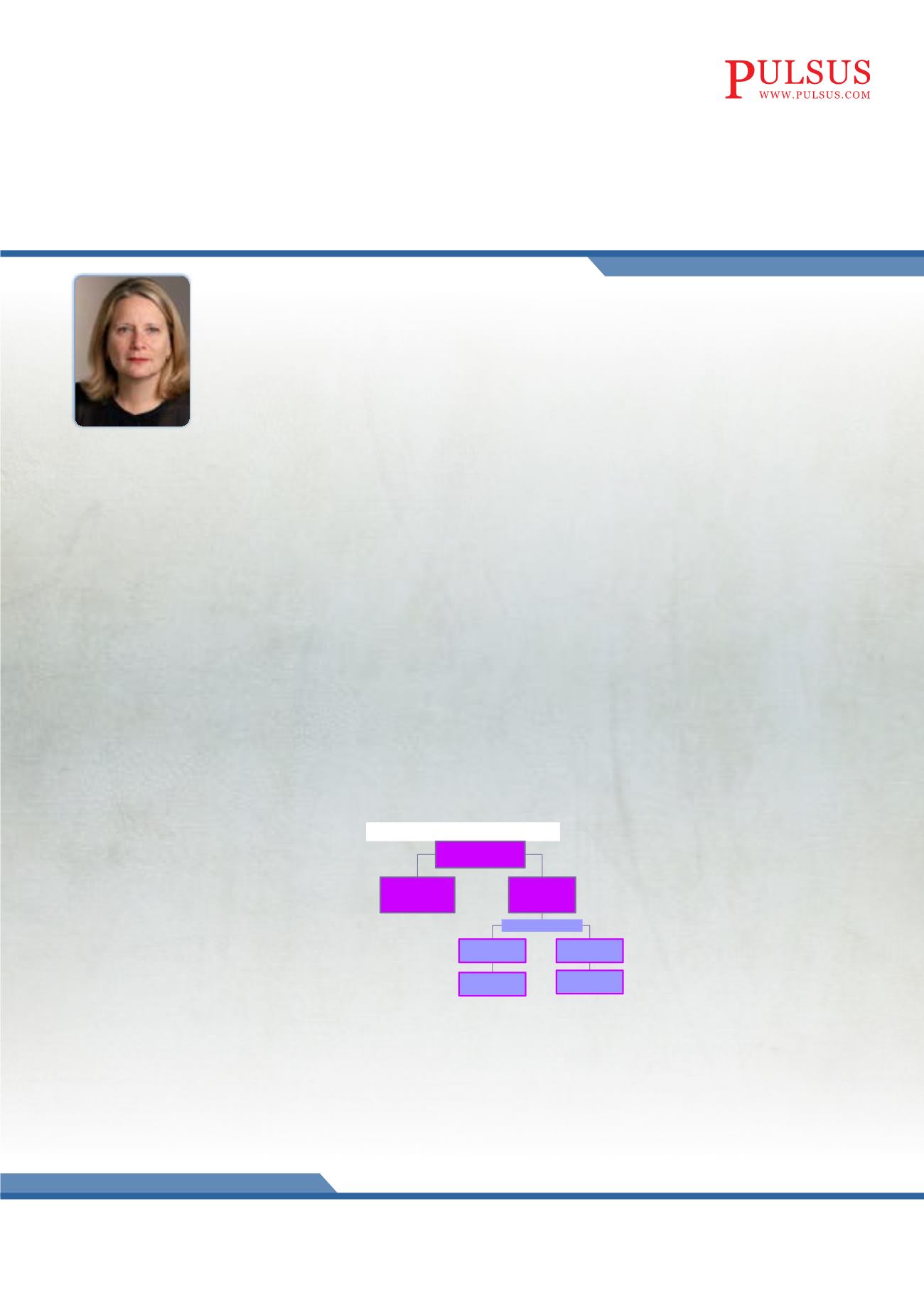
Figure 1 shows enrollment and completion rates of the study. Of the 8,400 food supplement ingestions, no infants
had any allergic reaction nor received any prescribed medication or medical care. Of 14,252 placebo ingestions,
1% (N=250) resulted and 0.7% (N=61) of food supplement ingestions in a report of symptoms (e.g., cough,
diarrhea). This study suggests that the food supplement is safe and feasible for infants. Future study should assess
the effect of the food supplement on immunologic responses to the allergenic proteins and on the incidence of
food allergy.
Biography
Jane L Holl is a General Pediatrician and Health Services and Outcomes Researcher who has conducted substantial prior research on childhood food allergy in
the US. She is the Director of the Center for Healthcare Studies, an interdisciplinary center at Northwestern University. She has partnered previously with Kay
Savio from Focus Pointe Global, Inc., a global market research company with fully vetted, precision-targeted participants.
j-holl@northwestern.eduJane L Holl
Northwestern University & Focus Pointe Global, Inc., USA
Figure 1. Enrollment and Completion Rates
405 (62%)
completed
placebo
245 (38%)
did not start or
discontinued
300
product
105
placebo
Randomization
260 (87%)
completed
94 (89%)
completed
650
received placebo