
Page 44
Volume 03
Spine 2019
October 16-17, 2019
Journal of Neurology and Clinical Neuroscience
October 16-17, 2019 | Rome, Italy
SPINE AND SPINAL DISORDERS
5
th
World Congress on
J Neurol Clin Neurosci, Volume 03
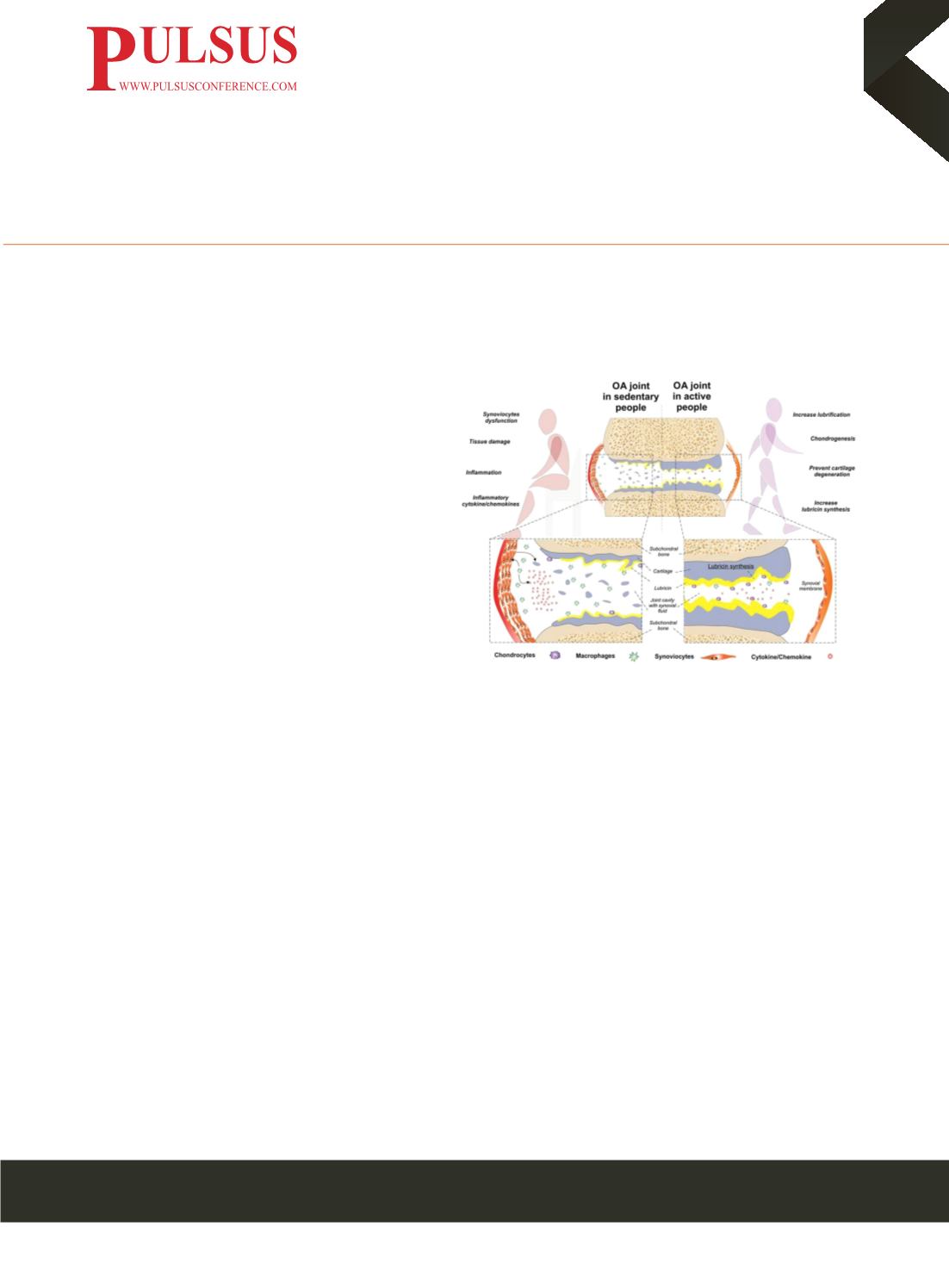
Physical activity as a non-pharmacologic treatment to be prescribed in osteoarthritis
Giuseppe Mususmeci
University of Catania, Italy
Purpose
: The purpose of this study was to investigate
the influence of Moderate Physical Activity (MPA)
on the expression of osteoarthritis (OA)-related (IL-
1, IL-6, TNF-α, MMP-13) and anti-inflammatory and
chondroprotective (IL-4, IL-10, lubricin) biomarkers in
the synovium of an OA-induced rat model. The MPA-
based approach may support joint tribology and synovial
lubrication, leading to improved joint function and pain
relief. In addition, in pathologic conditions, synoviocytes
type A secrete cathepsins, MMPs and pro-inflammatory
cytokines/chemokines into the extracellular matrix,
triggering tissue damage.
Methods
: A total of 32 rats were divided into four groups:
Control rats (Group 1); rats performing MPA (Group 2);
anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT)-rats with OA
(Group 3); and, ACLT-rats performing MPA (Group 4). Early OAwas induced through the anterior cruciate ligament transection
(ACLT) technique.Analyses were performed using Hematoxylin &Eosin staining, histomorphometry and immunohistochemistry.
Results
: In Group 3, OA biomarkers were significantly increased, whereas, IL-4, IL-10, and lubricin were significantly lower
than in the other groups. The results fromMPAexperimental group (Group 4) highlighted the decreased expression of OA-related
biomarkers (IL-1, TNF-α, MMP-13) and the increased expression of chondroprotective ones (IL-4, IL-10 and lubricin).
Conclusions
: We hypothesize that MPA might partake in rescuing Type B Synoviocyte Dysfunction at the early stages of OA,
delaying the progression of the disease and finally postponing the need for joint replacement.
e
:
g.musumeci@unict.it















