Page 19
Volume 3
Journal of Pharmacology and Medicinal Chemistry
Nanomedicine 2019
Biotechnology 2019
May 20-21, 2019
May 20-21, 2019 London, UK
4
th
World Biotechnology CONGRESS
Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology
4
th
International Conference on
&
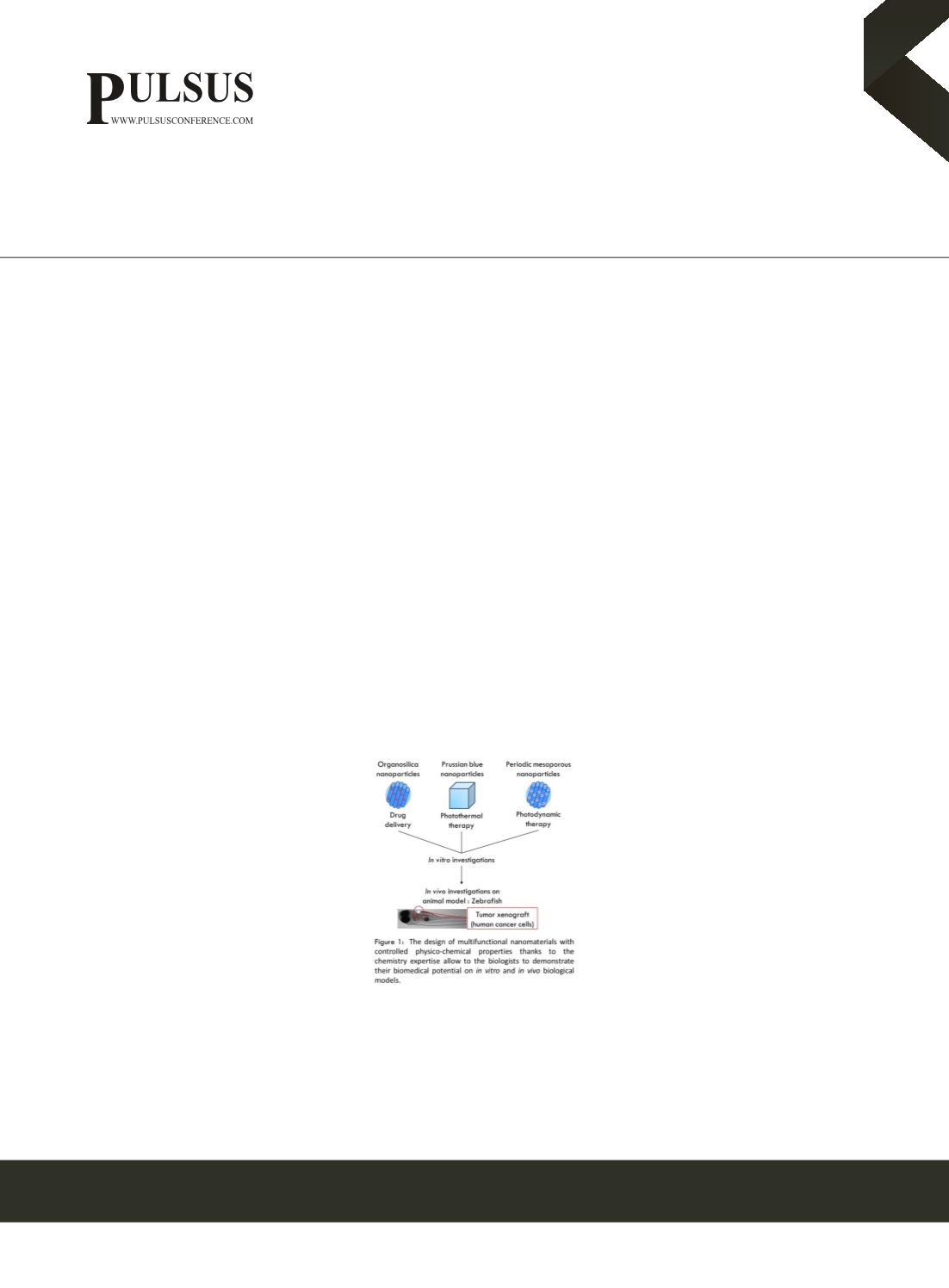
Development of versatile biological models to study nanodevices biomedical potential
Morgane Daurat
Institut des Biomolécules Max Mousseron, France
T
he development of personalized and non-invasive therapies based on new nanoparticles is a major challenge in medicine. In
this context, we studied different nanoparticles for cancer therapy.
Firstly, we analyzed the biological efficiency of hollow organosilica nanoparticles. Porous systems are used to be applied to
drug adsorption and delivery. In this case, we have loaded two anti-cancer drugs, which have been used to perform in vitro
investigations in order to demonstrate their biocompatibility and their potential as drug carrier vehicles to treat cancer.
Moreover, nanoscience has grown considerably in cancer treatment with nanoparticles activated with stimuli as Mn2+-doped
Prussian blue nanoparticles. They are many advantages as their flexible structure, porosity and biocompatibility. Indeed, Prussian
blue has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for human. We have demonstrated for the first time that these
nanoparticles acted as efficient agents for photothermal therapy under Two-Photon Excitation (TPE) and induce an almost
eradication of malignant cells.
Finally, in order to respond to increasing demand for new therapies, the PhotoDynamic Therapy (PDT) has arisen as an alternative
to chemo- and radiotherapy for the non-invasive selective destruction of small tumors. PDT is based on photosensitizers activation
by irradiation. To enhance the selectivity towards tumor cells and the efficiency of PDT, the photosensitizers are encapsulated
in Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica (PMO) nanoparticles. To go further in the biomedical proof of concept of therapeutic
nanoparticles, we are currently developing an animal model as Danio rerio (zebrafish) to study cancer. We have implanted
fluorescent human cancer cells in zebrafish larvae in order to establish a detectable tumor xenograft. Then, we have intravenously
injected PMO for TPE-PDT in zebrafish and irradiated the tumor site with a pulsed laser. The strong decrease in tumor size let us
imagine developing such model to test the biomedical potential of different nanoparticles.
Biography
Morgane Daurat is born in 1991 in Béziers (France). She is a PhD student in third year at Institut des Biomolécules Max Mousseron in
Montpellier (France). She works on the development of biological models to study nanoparticles biomedical potential and on lysosomal
diseases for the company NanoMedSyn (Montpellier, France). She is co-author of nine articles.
morgane.daurat@etu.umontpellier.frJ Pharmacol Med Cheml, Volume 3