
Page 38
Recycling 2019 & Material Science 2019
July 22-23, 2019
Volume 3
Journal of Environmental Geology
Material Science and Nanotechnology
Global Recycling Summit
July 22-23, 2019 | Rome, Italy
6
th
International Conference on
&
Structural, electronic, mechanical and thermodynamical properties of some double Perovskite oxides: A
DFT calculation
Vipul srivastava
Lovely Professional University, India
R
ecently, perovskites have been investigated with great attention both theoretically as well as experimentally in physics,
chemistry, and material science because of their variety of applications in science and technology. The double perovskites are
very important members of this diverse perovskite family having different structures, composition and physical properties in the
fieldsofspintronics,multiferroics,halfmetallic,ferromagnetic,magneto-dielectric,andmagneto-optics[1,2].Magnetically,double
perovskite family exhibits a wide range of magnetic behaviours[3]. Full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FP-LAPW)
method based upon density functional theory (DFT) as employed in WIEN2K has been used to calculate structure, electronic,
magnetic and thermodynamical properties. Structural investigation has been carried within GGA scheme of PBE. For electronic
(Fig.1a), magnetic and mechanical investigations GGA, GGA+U, mBJ approximations have been employed. These perovskites
occupy cubic structure with space group Fm-3m (225). Most of the double peroveskites show ferromagnetic nature and if spins are
plotted, interestingly, they show half-metallicity, which make these materials application in spintronic devices. Further, electronic
band profile of these materials depicted another feature used in indirect band gap semiconductors. The mechanical properties like
Young's modulus (Y), Poisson's ratio (n), Bulk modulus (B) and Shear modulus (G) have been also calculated from the value of
elastic constants. Furthermore, temperature and pressure dependent thermodynamic properties have also been calculated within
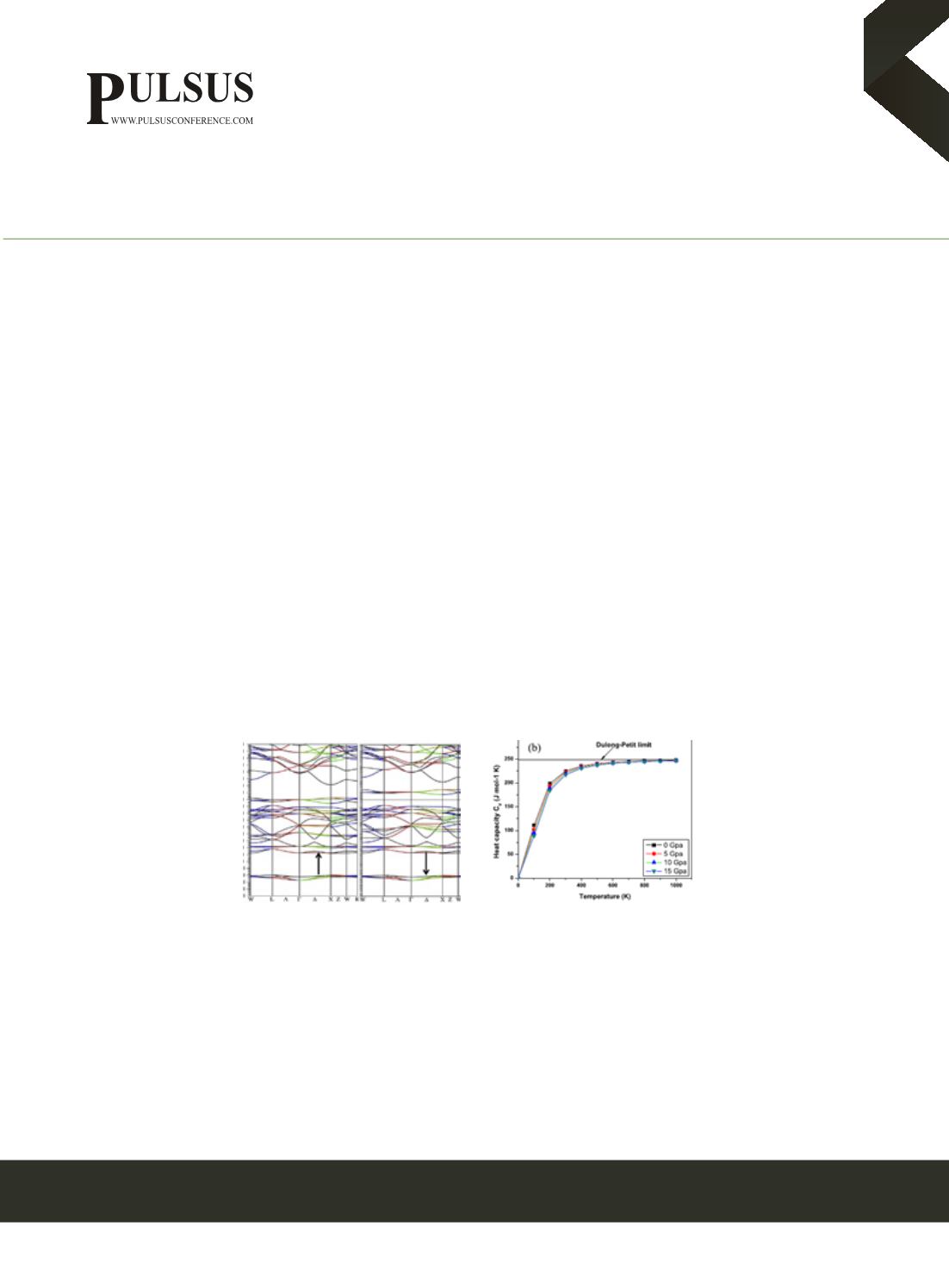
quasi-harmonic Debye approximation. We have plotted specific heat at constant volume (Cv) in Fig1b, thermal expansion (a),
Grüneisen parameter and Debye temperature. The Debye temperature can be used in describing the excitation of phonons and to
designate various lattice thermal phenomena while the Grüneisen parameter explains the phonons contribution to specific heat.
Fig.1 (a)Bandstructurealonghighsymmetrydirections showinghalf-metallicnature (b)variationofCvunder tempera-
ture reaching to Dulong-Petit limit Ba2CdOsO3
JEnvironGeol. |Volume3
ISSN:2591-7641
















